A) methane (CH4)
B) carbon dioxide (CO2)
C) chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
D) nitrous oxides (NO)
E) hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Maunder minimum during the Little Ice Age has been linked to
A) a period of low sunspot activity from 1645 to 1715.
B) changes in Earth's axial tilt (obliquity) .
C) a cooling of the Gulf Stream from rapid glacial melt in Greenland.
D) volcanic activity and multiyear changes in global circulation.
E) changes in Earth's orbital shape (eccentricity) .
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Seasonal fluctuations in CO2 emissions reflect
A) summer melting in the tundra.
B) geothermal activity,which is highest in the fall.
C) increased fuel use for home and building heat in winter months.
D) reduction of sea ice cover and associated decrease in albedo in the summer.
E) seasonal changes in vegetation cover.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an example of individuals and communities working to mitigate climate change?
A) tree planting in exchange for greenhouse gas credits
B) leaving the decision-making to elected officials
C) farmers using no-till agriculture
D) protecting and restoring natural habitats
E) using renewable energy sources
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The science that studies Earth's past climates is
A) climate change science.
B) meteorology.
C) paleoclimatology.
D) dendrochronology.
E) limnology
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As air temperatures increase,evaporation increases.Warmer temperatures also increase the capacity to absorb water vapor.More water vapor in the atmosphere accelerates the greenhouse effect.This is known as the
A) ice-albedo feedback.
B) water-vapor feedback.
C) permafrost-carbon feedback.
D) wildfire-carbon feedback.
E) CO2-weathering feedback.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is incorrect?
A) Carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations are growing more quickly today than is seen throughout most of the long-term climate record.
B) Scientists can say with 100% certainty that current climate change can be solely attributed to anthropogenic causes.
C) Increased atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) causes warming temperatures.
D) Human activities have increased the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
E) The rise of global temperatures causes global climate change.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Radiative forcing (climate forcing) refers to
A) the power of electromagnetic radiation per unit area.
B) the amount by which some perturbation causes Earth's energy balance to deviate from zero.
C) a measurement of solar radiation energy received on a given surface area.
D) the contribution of each greenhouse gas to global warming.
E) the amount of time,on average,a greenhouse gas resides in the atmosphere.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Milankovitch cycles refer to
A) changes in Earth-Sun relationships,namely the Earth's orbit around the sun,the Earth's axial rotation,and the Earth's axial tilt.
B) cyclical changes in solar irradiance caused by increases and decreases in sunspot activity.
C) increases and decreases in atmospheric gases and aerosols,primarily caused by natural activity such as volcanic activity and changes in net primary productivity.
D) tectonic changes in continental positions.
E) topographic changes from orogeny,erosion,and mass wasting.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The residence time of methane (CH4) in the atmosphere is
A) 50 to 200 years.
B) 45 days.
C) approximately 90 days.
D) 12 years.
E) 500 years.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following accurately describes 18O/16O ratios of ice sheets?
A) The higher the ratio of oceanic 18O to 16O,the cooler the temperature is because 18O will be locked up in ice sheets.
B) A higher ratio of oceanic 18O to 16O indicates a warmer period during which more 18O evaporates and precipitates onto ice sheets.
C) During periods of colder temperatures,the 18O/16O ratio is higher because only the 18O isotope is being evaporated.
D) During warmer periods,16O evaporates more readily and,therefore,the 18O/16O ratio is significantly lower than cooler periods.
E) During cooler periods,18O evaporates more readily and,therefore,the amount of 16O in glaciers is negligible.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Key Indicators of climatic warming
Which of the following is not a key indicator of present climate change?
Key Indicators of climatic warming
Which of the following is not a key indicator of present climate change?
A) increasing sea-surface temperatures
B) decreasing mass of glaciers and ice sheets
C) decreasing extent of sea ice
D) rising sea level
E) decreasing atmospheric water vapor
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fossil fuel burning accounts for over____ percent of CO2 emissions.
A) 10
B) 20
C) 50
D) 70
E) 85
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
![Global land-ocean temperature trends,1880-2015.The graph shows change in global surface temperatures relative to the 1951-1980 global average.The gray bars represent uncertainty in the measurements.Note the inclusion of both annual average temperature anomalies and 5-year mean temperature anomalies;together,they give a sense of overall trends.[Based on data from NASA/GISS;available at http:// climate.nasa.gov/vital-signs/global-temperature/.] Since 1880,global land-ocean temperatures have shown A) a warming trend. B) a cooling trend. C) an oscillation between warming and cooling. D) a cooling trend until 1950,then a rapid warming trend. E) no trend.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5538/11eab6b6_9b61_c383_a5f2_e171ecda3567_TB5538_00.jpg) Global land-ocean temperature trends,1880-2015.The graph shows change in global surface temperatures relative to the 1951-1980 global average.The gray bars represent uncertainty in the measurements.Note the inclusion of both annual average temperature anomalies and 5-year mean temperature anomalies;together,they give a sense of overall trends.[Based on data from NASA/GISS;available at http:// climate.nasa.gov/vital-signs/global-temperature/.]
Since 1880,global land-ocean temperatures have shown
Global land-ocean temperature trends,1880-2015.The graph shows change in global surface temperatures relative to the 1951-1980 global average.The gray bars represent uncertainty in the measurements.Note the inclusion of both annual average temperature anomalies and 5-year mean temperature anomalies;together,they give a sense of overall trends.[Based on data from NASA/GISS;available at http:// climate.nasa.gov/vital-signs/global-temperature/.]
Since 1880,global land-ocean temperatures have shown
A) a warming trend.
B) a cooling trend.
C) an oscillation between warming and cooling.
D) a cooling trend until 1950,then a rapid warming trend.
E) no trend.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
General circulation models (GCMs) of the atmosphere
A) are pre-computer based models that estimated atmospheric and oceanic circulation and are now being used to study climate change.
B) are highly simplistic models that use one or two variables to test the veracity of climate proxies,such as ice core and ocean sediment core samples.
C) are based on statistical three-dimensional grids that characterize portions of the atmosphere and ocean in terms of climate-related variables.
D) calculate the concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere based on data from weather stations located around the globe.
E) are a combined GIS and remote sensing technique to monitor atmospheric and ocean currents.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to models developed by NOAA,given the extreme,global sea level may rise as high as
A) 0.2 m (0.7 ft) .
B) 0.5 m (1.6 ft) .
C) 1.2 m (3.9 ft) .
D) 2.0 m (6.6 ft) .
E) 3.2 m (10.5 m) .
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
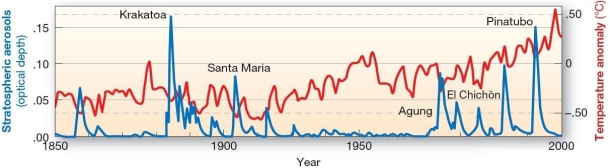 Temperature impacts of aerosols from volcanic eruptions
The graph shows that from 1850 to 2000,five large volcanic eruptions have
Temperature impacts of aerosols from volcanic eruptions
The graph shows that from 1850 to 2000,five large volcanic eruptions have
A) caused a sudden rise in global temperatures,often lasting a decade or more.
B) led to dramatic increases in regional temperatures over the past century.
C) increased the amount of acid deposition in areas surrounding the eruptions.
D) had no noticeable effects on global temperatures,only local and regional temperatures.
E) resulted in lowered global temperatures for several years.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
16O makes up approximately ____percent of all oxygen atoms.
A) 0.05
B) 0.2
C) 20.21
D) 50.33
E) 99.76
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Based on climate reconstructions,there is ample evidence that climates have fluctuated throughout Earth's long history.Describe some of the mechanisms of this climate fluctuations.
Correct Answer

verified
Several examples may include solar variability (sun spot activity),changes in Earth- Sun relationships (Milankovitch Cycles),plate tectonics and orogenies,and changes in concentrations of atmospheric gases and aerosols.
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Younger Dryas refers to
A) an interglacial period,characterized by a general warming trend,lasting since the last glacial maximum (LGM) to the present.
B) a global cooling episode,lasting from approximately A.D.1250 to 1850.
C) a brief return to near-glacial conditions during the transition period from the last glacial period to the present interglacial period.
D) a 400-year period,from A.D.800 to 1200,characterized by warmer than normal conditions in the North Atlantic region (e.g.Greenland and Iceland) .
E) any interglacial period lasting more the 100 years.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 92
Related Exams