A) I, II, and III
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) II and III only
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Public investment expenditure for highways, schools, and national defense is included in which component of GDP?
A) consumption
B) gross private investment
C) government purchases
D) public investment
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to Professor Baotai Wang who examined the crowding out phenomenon in Canada between 1961-2000, as discussed in the Case in Point, government expenditures for health and education
A) increased human capital and encouraged private sector investment, leading to crowding in.
B) did not increase the rate of return on private investment and therefore led to crowding out.
C) increased human capital and generated strong supply-side effects.
D) led to only small increases in human capital.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A reduction in tax rates may result in a short-term reduction in government revenues, but it will also leave people with more disposable income.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the federal budget is initially balanced and government expenditures remain constant, then a Decrease in GDP will
A) decrease tax revenues and create a budget surplus.
B) increase tax revenues and create a budget surplus.
C) decrease tax revenues and create a budget deficit.
D) increase tax revenues and create a budget deficit.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Fiscal policy is concerned with government's manipulation of taxing, spending, and the money supply to encourage full employment at stable prices.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the government institutes a new investment tax credit. This is likely to
A) shift the short-run aggregate supply curve to the right by an amount equal to the amount of tax credit times the spending multiplier.
B) shift the aggregate demand curve to the right by an amount equal to the amount of tax credit times the spending multiplier.
C) shift the short-run aggregate supply curve to the right by an amount equal to the initial change in investment times the spending multiplier.
D) shift the aggregate demand curve to the right by an amount equal to the initial change in investment times the spending multiplier.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Contractionary fiscal policy will lead to a fall in interest rates.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The use of government expenditures and taxes to influence the level of economic activity is called fiscal policy.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In general, personal income taxes
A) rise automatically during a recession.
B) rise automatically during an expansion.
C) rise automatically during a contraction.
D) are decreased during a recession through legislative actions of Congress.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The provision of aid to an individual who is not required to provide anything in exchange is called a transfer payment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Taxes assessed on firms and employees on wages and salaries earned are called
A) dividend taxes.
B) payroll taxes.
C) corporate profits taxes.
D) earned income taxes.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The bulk of federal receipts come from
A) property taxes and personal income tax.
B) personal income tax and from payroll taxes.
C) corporate income taxes and personal income tax.
D) personal income tax and property taxes.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Recognition lags in fiscal policy stem largely from
A) the fact that it takes time before a fiscal policy, such as a change in government purchases or a change in taxes, is agreed to and put into effect.
B) the fact that it takes time for a policy action to have its full effect on aggregate demand.
C) the difficulty of collecting economic data in a timely and accurate fashion.
D) households and businesses may not respond to fiscal policy to the extent that policy makers had hoped, for example, they may not be as responsive to a tax cut .
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes a discretionary fiscal policy action/program?
A) the progressive income tax system
B) The government increases funding for the Dislocated Worker Program, a federal initiative that provides retraining and career counseling.
C) the unemployment compensation program
D) the system of welfare programs
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some economists argue that
A) discretionary monetary policy is ineffective because of its long identification lag.
B) discretionary fiscal policy is ineffective because of its long recognition lag.
C) discretionary monetary policy is ineffective because of its long implementation lag.
D) discretionary fiscal policy is ineffective because of its long implementation lag.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Contractionary fiscal policy will lead to an increase in government borrowing.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An expansionary fiscal policy will result in the Treasury selling more bonds, the price of bonds falling, and interest rates rising.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An inflationary gap can be closed with
A) using an expansionary monetary policy.
B) using a policy action such as a reduction in taxes.
C) using a policy action such as a reduction in government purchases.
D) imposing price controls to prevent prices from rising.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 12-1 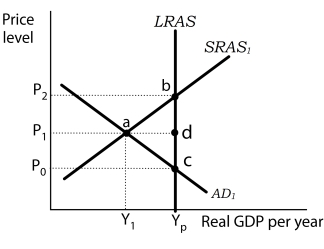 -Refer to Figure 12-1. At output level Y1,
-Refer to Figure 12-1. At output level Y1,
A) potential output is greater than actual output.
B) the economy is operating at a point outside its production possibilities curve.
C) the actual unemployment rate is less than the natural rate of unemployment.
D) aggregate demand will fall to restore equilibrium.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 181
Related Exams