A) a missing chromosome
B) a chromosome with a unique cytological marker
C) three chromosomes with identical structure
D) colored bands along the lengths of a chromosome
E) an extra chromosome
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cross GE/ge × ge/ge produces the following progeny: GE/ge 404; ge/ge 396; gE/ge 97; Ge/ge 103.From these data one can conclude that______ .
A) the recombinant progeny are Ge/Ge and gE/gE
B) the recombinant progeny are gE/ge and Ge/ge
C) the recombinant progeny are GE/GE and ge/ge
D) the recombinant progeny are gE/GE and GE/ge
E) the recombinant progeny are GE/ge and GE/ge
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In Drosophila,assume that the gene for scute bristles s) is located at map position 0.0 and that the gene for ruby eyes r) is at position 15.0.Both genes are located on the X chromosome and are recessive to their wild-type alleles.A cross is made between scute-bristled females and ruby-eyed males.Phenotypically wild-type F1 females were then mated to homozygous double mutant males,and 1000 offspring were produced.Give the frequency of scute expected.
A) 360
B) 500
C) 75
D) 425
E) 250
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a three-point mapping experiment,how many different genotypic classes are expected?
A) 1
B) 0
C) 8
D) 4
E) 2
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that the genes for tan body and bare wings are 15 map units apart on chromosome II in Drosophila.Assume also that a tan-bodied,bare-winged female was mated to a wild-type male and that the resulting F1 phenotypically wild-type females were mated to tan-bodied,bare-winged males.Of 1000 offspring,what would be the expected of wild-type offspring,and in what numbers would they be expected?
A) 75
B) 425
C) 50
D) 350
E) 8
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes why mapping is most accurate when genes are close together on a chromosome?
A) This is not true; mapping genes is most accurate when genes are far away from each other.
B) Double crossover events yield a result that looks the same as no crossover in a two gene mapping experiment and this throws off the calculations.
C) The centromere gets in the way.
D) This is not true; relative distance of two loci on a chromosome has no effect on accuracy of mapping.
E) Double crossover events yield a result that looks the same as one crossover in a two gene mapping experiment and this throws off the calculations.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The coefficient of coincidence reflects the frequency of observed double crossovers compared to the frequency of expected double crossovers.What is the relationship between the coefficient of coincidence and interference?
A) Interference equals the coefficient of coincidence.
B) Interference equals the coefficient of coincidence divided by the map units calculated.
C) Interference is the inverse square of the coefficient of coincidence.
D) Interference is one minus the coefficient of coincidence.
E) Interference is recombinants minus nonrecombinants.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Sister chromatid exchange would mutate one strand of DNA.
B) Harlequin chromosomes are a result of homologous recombination.
C) Sister chromatid exchange would lead to a reshuffling of alleles.
D) Crossing over has a cytological basis.
E) Exchanges occur between homologous chromosomes,but never between sister chromatids.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If interference is complete,what would be the frequency of double crossovers?
A) 0.75
B) 2
C) 0
D) 1
E) 0.25
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The phenomenon in which one crossover decreases the likelihood of crossovers in nearby regions is called________ .
A) negative interference
B) reciprocal genetic exchange
C) mitotic recombination
D) positive interference
E) chiasma
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cross GE/ge × ge/ge produces the following progeny: GE/ge 404; ge/ge 396; gE/ge 97; Ge/ge 103.From these data,one can conclude that .
A) the G and E loci are segregating independently
B) the G and E loci are linked
C) the G and E loci reside on the same chromosome over 50 map units apart
D) the G and E loci show complete linkage
E) the G and E loci assort independently
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that a cross is made between AaBb and aabb plants and that the offspring occur in the following numbers: 106 AaBb,48 Aabb,52 aaBb,94 aabb.These results are consistent with which scenario described?
A) It is impossible to tell.
B) There is a very high coefficient of coincidence.
C) The genes are unlinked.
D) In the AaBb parent,the dominant alleles are on one homolog and the recessive alleles are on the other.
E) In the AaBb parent,each homolog has one dominant allele and one recessive allele.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The genes for purple eyes and curved wings are approximately 21 map units apart on chromosome II in Drosophila.Assume that a purple-eyed female was mated to a curved wing male and that the resulting F1 phenotypically wild-type females were mated to purple,curved males.Of 1000 offspring,what would be the expected number of flies with purple eyes and curved wings?
A) 540
B) 395
C) 210
D) 790
E) 105
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What term is applied when two genes fail to assort independently,that is,they tend to segregate together during gamete formation?
A) tetrad analysis
B) Mendelian inheritance
C) discontinuous inheritance
D) dominance and/or recessiveness
E) linkage
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Below is a diagram during crossing over.Describe the outcome. 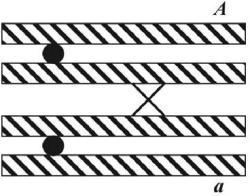
A) offspring will not look like either parent
B) a 1:1 ratio
C) formation of parental alleles only
D) segregation of alleles A and a during meiosis II
E) segregation of alleles A and a during meiosis I
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that there are 12 map units between two loci in the mouse and that you are able to microscopically observe meiotic chromosomes in this organism.If you examined 200 primary oocytes,in how many would you expect to see a chiasma between the two loci mentioned above?
A) 96
B) 48
C) 6
D) 12
E) 24
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What relatively recent scientific advancement has made mapping by linkage or classical genetic mapping approaches virtually obsolete?
A) the inclusion of the X and Y chromosomes in SNP experiments
B) positive interference
C) the use of synteny
D) negative interference
E) the genome sequence of a species
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A ____ is all the genes on a single chromosome.
A) chromosomal conglomeration
B) gene loci line
C) genetic allele formation
D) linkage group
E) recombination group
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
__________occurs when a crossover in one region of a chromosome reduces crossovers in nearby regions.
A) Triple crossover
B) Negative supercoiling
C) Coefficient of coincidence
D) Positive interference
E) Negative interference
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that investigators crossed a strain of flies carrying the dominant eye mutation Lobe on the second chromosome with a strain homozygous for the second chromosome recessive mutations smooth abdomen and straw body.The F1 Lobe females were then backcrossed with homozygous smooth abdomen,straw body males,the following phenotypes were observed: 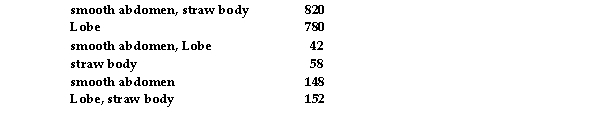 Give the map units between Lobe and straw.
Give the map units between Lobe and straw.
A) 15
B) 7.5
C) 10
D) 20
E) 5
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 43
Related Exams