A) steeper and the multiplier larger.
B) steeper and the multiplier smaller.
C) flatter and the multiplier larger.
D) flatter and the multiplier smaller.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The assertion that consumption depends on expected average annual income is called
A) permanent income.
B) the current income hypothesis.
C) current income.
D) the permanent income hypothesis.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the consumption function is C = $500 + 0.8Y. If Y = $1,000, then autonomous consumption is
A) $500.
B) $800.
C) $1,000.
D) $1,300.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in autonomous aggregate expenditures
A) causes a movement along the aggregate expenditures curve.
B) causes a movement along the aggregate demand curve.
C) increases the value of the multiplier.
D) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Let AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption, IP = Planned Investment, G =Government Purchases. Consider a simple aggregate expenditures model, where AE = C + IP + G and all components of aggregate expenditures except consumption are autonomous. If the MPS is 0.4, then the multiplier is
A) 1.33
B) 2.5
C) 5
D) 15
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions .
Exhibit: Aggregate Expenditures Curve
Figure 13-6 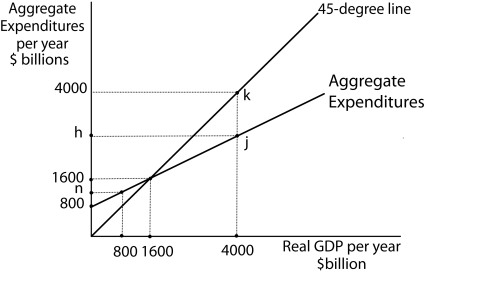 -(Exhibit: Aggregate Expenditures Curve) Let Y = real GDP, AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption, IP = Planned Investment, G = Government Purchases. Further, IP and G are autonomous. What is the equation of the aggregate expenditures curve? All figures in billions of dollars.
-(Exhibit: Aggregate Expenditures Curve) Let Y = real GDP, AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption, IP = Planned Investment, G = Government Purchases. Further, IP and G are autonomous. What is the equation of the aggregate expenditures curve? All figures in billions of dollars.
A) AE = G + IP
B) AE = 800 + G + IP
C) AE = 800 + G + IP + 0.5Y
D) AE = 800 + 0.5Y
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An increase in the slope of the aggregate expenditures curve leads to a decrease in the value of the multiplier.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Let AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption, IP = Planned Investment, G = Government Purchases. Consider a simple aggregate expenditures model, where AE = C + IP + G and all components of aggregate expenditures except consumption are autonomous. All other things unchanged, a decrease in the price level
A) shifts the aggregate expenditures curve upwards.
B) shifts the aggregate expenditures curve downwards.
C) causes a movement up along a given aggregate expenditures curve.
D) causes a movement down along a given aggregate expenditures curve.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a simple aggregate expenditure model where all components of aggregate expenditure are autonomous except consumption. If government purchases increases by $200 billion, the aggregate expenditures curve will shift up by
A) $200 billion.
B) $200 billion *the multiplier.
C) $200 billion * marginal propensity to consume.
D) $200 billion *(1 ÷ marginal propensity to consume) .
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions .
Exhibit: Consumption Functions
Figure 13-3 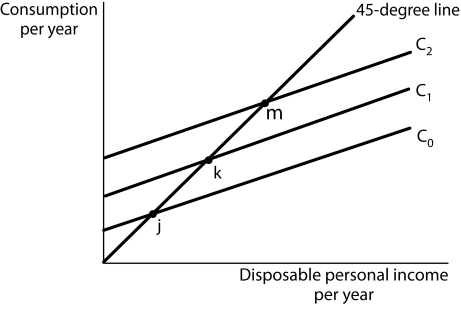 -(Exhibit: Consumption Functions) Which of the following statements is false?
-(Exhibit: Consumption Functions) Which of the following statements is false?
A) At points j, k, and m, consumers spend all their disposable income on consumption.
B) The amount of consumption is positive even when disposable income equals zero.
C) The slope of the consumption function is the marginal propensity to consume.
D) At points j, k, and m, the marginal propensity to save equals zero.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the economy spends 80% of any increase in real GDP, then an increase in autonomous investment of $1 billion would result ultimately in an increase in equilibrium real GDP of
A) $0.8 billion.
B) $1.0 billion.
C) $1.8 billion.
D) $5.0 billion.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions .
Exhibit: Aggregate Expenditures and Real GDP 2 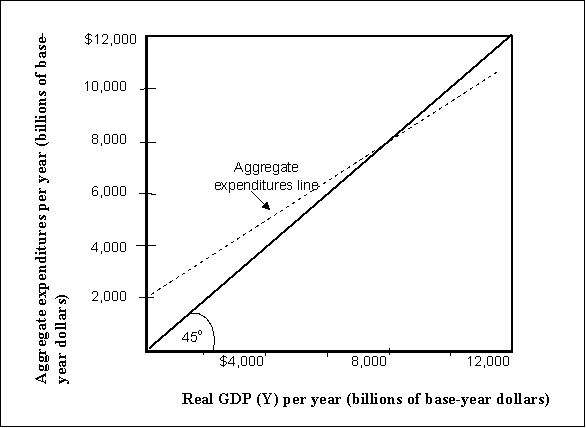 -(Exhibit: Aggregate Expenditures and Real GDP 2) Let Y = real GDP, AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption, IP = Planned Investment. Consider a simple economy where AE = C + IP, and IP is autonomous. What is the value of AE when Y = $12,000 billion?
-(Exhibit: Aggregate Expenditures and Real GDP 2) Let Y = real GDP, AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption, IP = Planned Investment. Consider a simple economy where AE = C + IP, and IP is autonomous. What is the value of AE when Y = $12,000 billion?
A) $2,000 billion
B) $8,000 billion
C) $11,000 billion
D) $12,000 billion
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions .
Exhibit: Aggregate Expenditures and Real GDP 2  -(Exhibit: Aggregate Expenditures and Real GDP 2) Let Y = real GDP, AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption, IP = Planned Investment. Consider a simple economy where AE = C + IP, and IP is autonomous. What is the value of autonomous AE?
-(Exhibit: Aggregate Expenditures and Real GDP 2) Let Y = real GDP, AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption, IP = Planned Investment. Consider a simple economy where AE = C + IP, and IP is autonomous. What is the value of autonomous AE?
A) $2,000 billion
B) $3,000 billion
C) $4,500 billion
D) $8,000 billion
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy spends 90% of any increase in real GDP, then an increase in autonomous investment of $1 billion would result ultimately in an increase in equilibrium real GDP of
A) $1.0 billion.
B) $1.9 billion.
C) $10 billion.
D) $100 billion.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions .
Exhibit: Aggregate Expenditures Curve
Figure 13-6  -(Exhibit: Aggregate Expenditures Curve) What is the value of the multiplier?
-(Exhibit: Aggregate Expenditures Curve) What is the value of the multiplier?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 5
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions .
Exhibit: Aggregate Expenditures and Real GDP 1 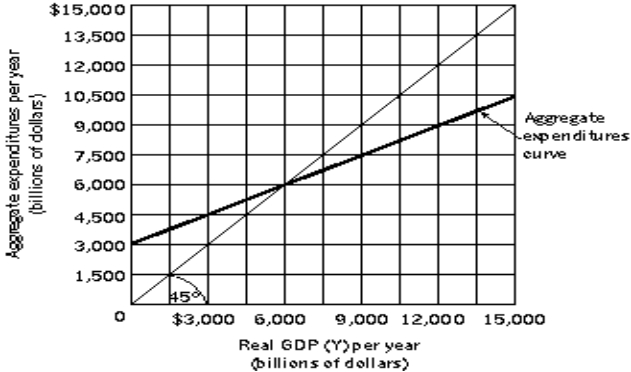 -(Exhibit: Aggregate Expenditures and Real GDP 1) Let Y = real GDP, AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption, IP = Planned Investment. Suppose AE = C + IP, and IP is autonomous. If the level of real GDP equals $5,000 billion, and if there are no changes in the consumption function or in planned investment, then we can expect that, in the next period, real GDP will
-(Exhibit: Aggregate Expenditures and Real GDP 1) Let Y = real GDP, AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption, IP = Planned Investment. Suppose AE = C + IP, and IP is autonomous. If the level of real GDP equals $5,000 billion, and if there are no changes in the consumption function or in planned investment, then we can expect that, in the next period, real GDP will
A) rise.
B) remain unchanged.
C) fall.
D) fall, but only if there is an offsetting change in autonomous consumption.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a simple aggregate expenditure model where all components of aggregate expenditure are autonomous except consumption. If the consumption function is C = $500 + 0.8Y, planned investment = $200, government purchases = $300, Net exports = $100, and real GDP = $1,000, what is the amount of autonomous expenditures?
A) $500
B) $1,000
C) $1,100
D) $1,900
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Let AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption, IP = Planned Investment, G = Government Purchases. Consider a simple aggregate expenditures model, where AE = C + IP + G and all components of aggregate expenditures except consumption are autonomous. All other things unchanged, an increase in the price level,
A) causes a movement up along a given aggregate expenditures curve and raises the equilibrium real GDP.
B) causes a movement down a given aggregate expenditures curve and lowers the equilibrium real GDP.
C) shifts the aggregate expenditures curve upwards and raises the equilibrium real GDP.
D) shifts the aggregate expenditures curve downwards and lowers the equilibrium real GDP.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Let AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption, IP = Planned Investment, G =Government Purchases. Consider a simple aggregate expenditures model, where AE = C + IP + G, and all components of aggregate expenditures except consumption are autonomous. In this model, the multiplier is found using the formula
A) ∆Y* ÷ initial ∆AE where Y* = equilibrium real GDP by the ∆ = change in, AE = aggregate expenditures.
B) ∆AE ÷ ∆Y*.
C) ∆Y* * MPC where MPC = marginal propensity to consume.
D) 1 ÷ MPC.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Autonomous aggregate expenditures are those that automatically vary with real GDP,whereas induced expenditures only change in response to a change in an external factor.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 219
Related Exams