A) equilibrium level without affecting employment.
B) equilibrium level and an increase in employment.
C) competitive level and all workers will gain.
D) competitive level without a pool of unemployed workers seeking to work at the higher wage.
E) competitive level but will reduce the level of employment.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows the supply and demand for labour in a hypothetical town in northern British Columbia,with only one employer,a logging company.
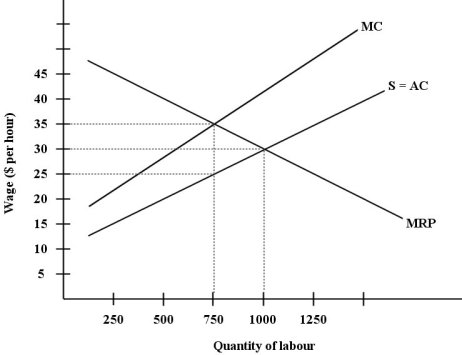 FIGURE 14- 4
-Suppose that the professional association of dentists reduces entry into their profession by lengthening the required training program.The likely effect is that
FIGURE 14- 4
-Suppose that the professional association of dentists reduces entry into their profession by lengthening the required training program.The likely effect is that
A) the supply curve of dentists will shift to the right.
B) the supply curve of dentists will shift to the left.
C) there will be an increase in the quantity of dentists supplied.
D) the demand curve for dentists will shift to the right.
E) both the demand and supply curves for dentists will shift to the left.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose there is a competitive market for retail workers at a large shopping mall that is large enough to constitute its own labour market.The labour demand curve is QD = 1000 - 20(w) .The labour supply curve is QS = 400 + 40(w) .Suppose that a union now successfully organizes the workers at this mall and obtains a wage rate of $13 (but does not affect the position of the demand curve) .One result is
A) an increase in employment of 20 workers.
B) a decrease in employment of 140 workers.
C) a decrease in employment of 100 workers.
D) an increase in employment of 60 workers.
E) a decrease in employment of 60 workers.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Certain professions limit the number of students who are eligible to enroll in their programs in university - engineering,architecture,dentistry,and law,for example.What is the predicted effect of such a policy in each of these professions?
A) A reduction in supply and a wage that is lower than it otherwise would be.
B) An increase in supply and a wage that is lower than it otherwise would be.
C) These professions are a relatively small portion of the labour market and so there will be no detectible change in wages.
D) An increase in supply and a wage that is higher than it otherwise would be.
E) A reduction in supply and a wage that is higher than it otherwise would be.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows the labour demand and labour supply schedules in a competitive labour market. TABLE 14- 1 -Investment in human capital can be very costly to the individual,but it can also generate large returns.Canadian census data from 2007 show that average employment income for a university graduate is approximately of the average employment income of a worker with no more than a high school diploma.
A) 400%
B) 50%
C) 300%
D) 125%
E) 200%
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following statements describe the adverse effects suffered by groups subject to labour- market discrimination.Which of the statements is false?
A) They will be more likely to experience spells of unemployment.
B) They will receive lower wages on average than other groups.
C) The discriminatory wage differentials will persist as long as the discrimination exists.
D) Their human capital will increase.
E) Their children's ability and willingness to invest in human capital will be less on average than those of children of other groups.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As a seller of labour services,a labour union is a form of
A) monopsony.
B) monopolistic competitor.
C) monopoly.
D) illegal cartel.
E) oligopoly.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The purpose of a labour union is to
A) increase employment in its industry.
B) exploit its labour- market power in the same way a monopolist exploits its market power in labour markets.
C) exploit its labour- market power in the same way a monopolist exploits its market power in product markets.
D) decrease employment in its industry.
E) maintain a minimum level of employment.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows the labour demand and labour supply schedules in a competitive labour market. TABLE 14- 1 -Refer to Table 14- 1.In a competitive labour market,a legislated minimum wage imposed at $10 per hour would
A) lead to an employment level lower than the competitive level.
B) have no effect on the competitive equilibrium level of employment.
C) lead to an equilibrium wage higher than the competitive wage.
D) lead to unemployment of 500 hours/month.
E) lead to over- employment of 500 hours/month.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about minimum- wage laws is most accurate?
A) There is some evidence that minimum- wage laws create a lot of jobs,particularly among youths.
B) All Canadian provinces have the same minimum wage.
C) Minimum- wage laws only affect the income of the higher- skilled,lowest- wage workers.
D) Minimum- wage laws are unfair.
E) There is some evidence that minimum- wage laws cause additional unemployment,particularly among youths.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the 1950s and 1960s,Arvida,Quebec,was basically a one- company town where Alcan was the sole buyer of labour services.This is a good example of
A) monopsony.
B) union power.
C) pure monopoly.
D) oligopoly.
E) monopolistic competition.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose there is a competitive market for retail workers at a large shopping mall that is large enough to constitute its own labour market.The labour demand curve is QD = 1000 - 20(w) .The labour supply curve is QS = 400 + 40(w) .Suppose that a union now successfully organizes the workers at this mall and obtains a wage rate of $11 (but does not affect the demand curve) .The number of workers employed after unionization is
A) 1000.
B) 880.
C) 780.
D) 400.
E) Not determinable from the information provided.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
FIGURE 14- 5 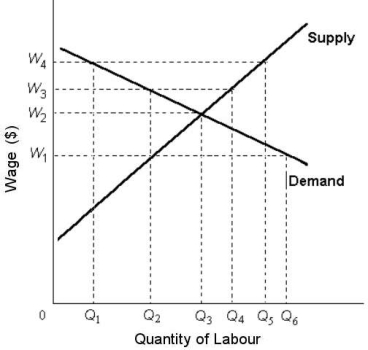 -Refer to Figure 14- 5.Suppose this labour market is competitive.If a minimum wage of W4 is then imposed,the quantity of labour supplied would be
-Refer to Figure 14- 5.Suppose this labour market is competitive.If a minimum wage of W4 is then imposed,the quantity of labour supplied would be
A) Q1.
B) Q2.
C) Q3.
D) Q4.
E) Q5.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below shows the supply and demand for labour in a hypothetical town in northern British Columbia,with only one employer,a logging company.
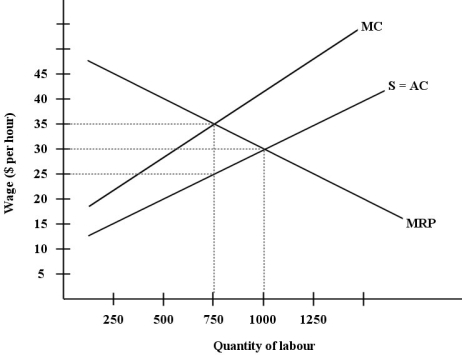 FIGURE 14- 4
-Refer to Figure 14- 4.Suppose this labour market is in a monopsonistic equilibrium.Then,suppose the provincial government of British Columbia imposes a minimum wage for employees in this industry of $38 per hour.What will be the effects on wages and employment?
FIGURE 14- 4
-Refer to Figure 14- 4.Suppose this labour market is in a monopsonistic equilibrium.Then,suppose the provincial government of British Columbia imposes a minimum wage for employees in this industry of $38 per hour.What will be the effects on wages and employment?
A) wages will rise by $8 per hour and employment will fall by between 0 and 250 units of labour
B) wages will rise by $3 per hour and employment will fall by 125 units of labour
C) wages will rise by $8 per hour and employment will remain unchanged
D) wages will rise by $13 per hour and employment will fall below 750 units of labour
E) wages will rise by $8 per hour and employment will fall below 750 units of labour
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that a regional health authority is the only employer of nurses,and further,suppose that nurses are not unionized.The 625 currently employed nurses are paid $27 per hour.To attract an additional nurse,the employer must increase the wage to $28 per hour.The marginal cost of this additional worker is
A) $27
B) $17 500
C) $28
D) $653
E) $17 528
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose your firm is a monopsonist hiring only one variable input.If you want to maximize profits,you will purchase that variable input up to the point where the
A) cost of the input equals the profit generated by the employment of that input.
B) demand curve intersects the supply curve of the input.
C) marginal product of that input equals the price of one unit of the input.
D) wage rate is the highest.
E) MRP curve for the input intersects the marginal cost curve for the input.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
FIGURE 14- 6 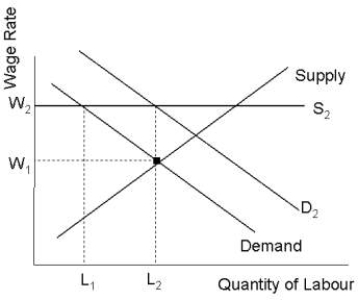 -Suppose market E discriminates against one group of workers and market O does not.Unemployment in market O would result if
-Suppose market E discriminates against one group of workers and market O does not.Unemployment in market O would result if
A) there is no statutory minimum wage.
B) the supply curve in market O shifts to the left and wages are slow to adjust.
C) the demand curve in market O shifts to the right and wages are slow to adjust.
D) the free- market equilibrium wage in market O is below the legal minimum wage.
E) some workers are unwilling to work in E- market jobs.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unions currently represent government employees in Canada.
A) approximately half of the
B) all of the
C) less than 10% of
D) less than 30% of
E) over 70% of
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In Canada in 2011,the share of total employment in agriculture was about
A) 20%.
B) 50%.
C) 0.2%.
D) 10%
E) 2%.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some people are concerned that "good" manufacturing jobs are being replaced by "bad" service- sector jobs.Why is this not necessarily a problem?
A) Average real per capita income has continued to rise,despite the rise of the service sector.
B) The decline in manufacturing employment is partly due to increasing productivity in that sector.
C) Consumers have an increased demand for services as real income increases.
D) Productivity increases in the service sector are likely underestimated.
E) all of the above
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 106
Related Exams