A) 20 to 40 bpm
B) 40 to 60 bpm
C) 60 to 100 bpm
D) 100 to 150 bpm
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the electrical impulse is initiated at the midpoint of the AV junction, where would you expect the P waves to appear on the ECG tracing?
A) Before the QRS complex
B) After the QRS complex
C) Within the QRS complex
D) P waves are absent entirely
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following originates from the AV junction?
A) Atrial flutter
B) Premature atrial complex
C) Junctional escape rhythm
D) Sinus bradycardia
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is it unlikely that a patient would have symptoms of low cardiac output with accelerated junctional rhythm?
A) The heart rate is the same as normal sinus rhythm.
B) The heart rate is influenced by the respiratory cycle and variations of vagal tone.
C) The rhythm originates at the AV junctional tissue, producing retrograde depolarization of atrial tissue.
D) The heart rate is slower than normal and loses the atrial kick.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the term for a condition in which a patient's blood pressure is not adequate to maintain good blood supply to the vital organs?
A) Hypoxia
B) Hyperventilation
C) Hypotension
D) Hypertension
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is one criterion for classifying a dysrhythmia as an SVT?
A) A wide QRS complex
B) Heart rate between 150 and 250 bpm
C) Identical atrial and ventricular rates
D) A clear, easily identifiable P wave
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the best definition of reentry dysrhythmias?
A) Abnormal slowing of conduction through the bundle of His
B) Blockage or short circuit of the normal electrical conduction pathway
C) Ischemia around the SA node
D) Ectopic impulses originating in the Purkinje network
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a single early electrical impulse that originates in the AV junction, occurring before the next expected sinus impulse and causing an irregularity in the rhythm?
A) Junctional tachycardia
B) SVT
C) PJC
D) Junctional escape rhythm
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which dysrhythmia does not have a consistent PR interval that measures less than 0.12 seconds?
A) Junctional escape rhythm
B) Accelerated junctional rhythm
C) Supraventricular tachycardia
D) Junctional tachycardia
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What symptoms might occur in a patient with junctional escape rhythm?
A) Hypertension, lung congestion, and syncope
B) Hypotension, confusion, and disorientation
C) Chest pain, lung congestion, and palpitations
D) Hypotension, nausea, and syncope
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In junctional rhythms, where does the electrical current initiate?
A) AV junction
B) Bundle of His
C) Atria
D) Ventricles
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The effect of junctional tachycardia on the patient depends on ________.
A) The force of the ventricular contractions
B) The rate of the rhythm
C) The timing of the atrial contractions
D) The atrial kick
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Junctional rhythms occur because the electrical impulse comes from the AV junction instead of the ________.
A) Purkinje fibers
B) Ventricles
C) Bundle of His
D) SA node
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What symptoms will a patient have if PJCs occur more than four to six times per minute?
A) Hypertension, rapid pulse
B) Chest pain, lung congestion
C) Pale skin, rapid breathing
D) Hypotension, irregular pulse
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of rhythm occurs when the SA node fails to initiate the electrical activity and one of the backup pacemaker sites takes over?
A) Junctional escape rhythm
B) Heart block rhythm
C) Asystole
D) Normal sinus rhythm
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are the distinguishing characteristics of junctional escape rhythm?
A) The rhythm is regular; the P wave may occur before, during, or after the QRS; and the P wave is inverted.
B) The rhythm is irregular, the P wave is inverted, and the P wave may immediately precede or follow the QRS complex.
C) The P wave may occur simultaneously with the T wave or may occur before, during, or after the QRS complex.
D) The P waves cannot be identified, there is chaotic electrical activity, and f waves may be seen.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the underlying rhythm in the ECG tracing shown here? 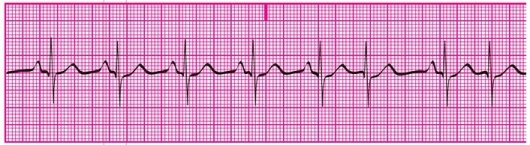
A) Normal sinus rhythm
B) Accelerated junctional rhythm
C) Junctional tachycardia
D) SVT
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the origination point of an SVT?
A) Left ventricle
B) Atria or junctional region
C) Purkinje fibers
D) Right ventricle
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the normal, inherent rate of the AV node?
A) 20 to 40 bpm
B) 40 to 60 bpm
C) 80 to 100 bpm
D) 100 to 150 bpm
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the following rhythm: 
A) Atrial fibrillation
B) Atrial flutter
C) Junctional tachycardia
D) SVT
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 51
Related Exams