B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Carboxypetidase A is a highly folded,globular protein that functions as a protease enzyme.Which of the following is a likely assumption about the amino acid residues that exist on the exterior of this folded protein?
A) The majority of these amino acids have disulfide bonds between cysteine residues.
B) The majority of these amino acids are hydrophilic in nature.
C) The majority of these residues are glycine.
D) None of these residues is serine.
E) The majority of these residues are nonpolar in nature.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Binding of a negative effector converts an active site on an enzyme into the active configuration.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sucrase is an example of an enzyme that displays absolute specificity.What does the term "absolute specificity" indicate about an enzyme?
A) It catalyzes the reaction of only a single substrate.
B) It catalyzes the reaction of only one class of compounds.
C) It catalyzes one type of reaction for the same class of compounds.
D) It catalyzes the reaction of only a single enantiomer of a compound.
E) It catalyzes the reaction of only a single type of bond.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Many enzymes are destroyed if the temperature rises significantly above 37ºC.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a class of enzymes?
A) isomerases
B) transferases
C) carnases
D) lyases
E) ligases
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the function of a lyase enzyme?
A) to catalyze redox reactions
B) to catalyze the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another
C) to catalyze hydrolysis reactions
D) to catalyze the addition of a group to a double bond or the removal of a group to form a double bond
E) to catalyze the formation or cleavage of a C-C,C-S,C-O,or C-N bond
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes the function of the enzyme cis-trans isomerase?
A) It breaks the double bond in an unsaturated fatty acid.
B) It converts pentose sugars to hexose sugars.
C) It converts between isomers on a disubstituted benzene ring.
D) It converts between the boat and chair conformations of a cyclohexane.
E) It breaks and re-forms a double bond to change the arrangement of the groups around a double bond.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction initially increases with an increase in the substrate concentration,but eventually reaches a maximum value,even though the concentration of substrate continues to increase.Which of the following best explains why?
A) As substrate concentration increases,the substrates preferentially bind with each other instead of the active site of the enzyme,and no additional catalysis occurs.
B) As substrate concentration increases,the active sites of all the enzyme molecules become occupied with substrate molecules,and no additional binding can occur.
C) An increase in substrate concentration eventually increases the temperature of the reaction mixture,and the enzyme becomes denatured.
D) An increase in substrate concentration allows for greater competition between substrate and inhibitor binding,and enzyme activity ceases.
E) When substrate concentrations become too high,local variations of pH occur that cause the enzyme to become denatured.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The arrival of a nerve impulse at the end plate of the nerve axon results in an influx of what ion?
A) calcium
B) sodium
C) potassium
D) bicarbonate
E) phosphate
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At extremes of pH,an enzyme will lose its biologically active conformation.What term describes the state of the enzyme under these conditions?
A) denatured
B) acidic
C) basic
D) buffered
E) noncovalent
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The penicillin class of antibiotics is inhibitors of an enzyme responsible for the formation of bacterial cell walls.The penicillin covalently binds to a serine residue in the active site of the enzyme,as depicted below.What type of bond is formed between the penicillin and the active site? 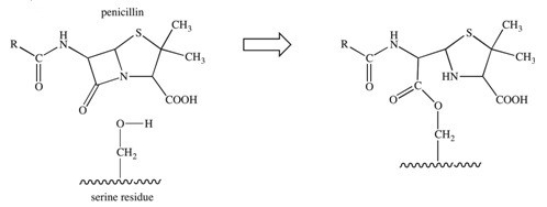
A) hydrogen bond
B) ionic bond
C) glycosidic linkage
D) ester bond
E) acetal bond
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The enzyme fumarase is a lyase enzyme that catalyzes the hydration of fumarate to give malate.What is the structure of malate? 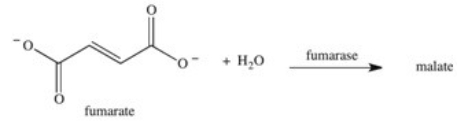
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of enzyme regulation occurs when the final product of a pathway shuts off the entire pathway for its own synthesis?
A) irreversible inhibition
B) competitive inhibition
C) feedback inhibition
D) poisoning
E) noncompetitive inhibition
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following will NOT destroy an enzyme by denaturation?
A) increase in temperature above 37°C (body temperature)
B) decrease in temperature below 37°C
C) significant increase in pH
D) significant decrease in pH
E) All of the choices will destroy an enzyme.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The presence of an enzyme will alter the relative ratio of product to reactant for a biochemical reaction.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes how an enzyme can affect the transition state in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
A) modifying the local pH by accepting or donating H+ ions
B) placing stress on a bond in the substrate,making it easier to break
C) bringing two reactants together in close proximity and in a suitable orientation for reaction
D) None of the choices are correct.
E) All of the choices are correct.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The enzyme acetylcholinesterase catalyzes the hydrolysis of acetylcholine.Which of the following is a product of this hydrolysis reaction? 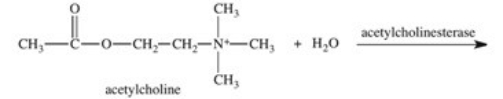
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Proteases,or proteolytic enzymes,are responsible for which of the following functions?
A) formation of the zwitterion form of a protein
B) hydrolysis of the ester bonds in dietary triglycerides
C) hydrolysis of the peptide bonds between amino acids in proteins
D) formation of the glycosidic linkages in disaccharides and polysaccharides
E) formation of bacterial cell walls
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lactase is an enzyme that catalyzes the following reaction.Which statement describing this reaction is FALSE? 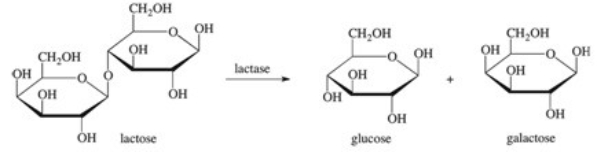
A) Lactose is the substrate in this reaction.
B) Glucose is a product in this reaction.
C) Galactose is a cofactor in this reaction.
D) This reaction occurs in the active site of lactase.
E) Lactase is a hydrolase enzyme.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 74
Related Exams