A) 0.23
B) 0.25
C) 0.28
D) 0.30
E) 0.32
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Modern nuclear bomb tests have created an extra high level of 14C in our atmosphere. Suppose that future archaeologists date samples from our era, but do not know about this testing. Will their dates be too young, too old, or still correct? If correct they are correct, why?
A) too young
B) too old
C) correct, because 14C from bomb tests is different from that produced naturally
D) correct, because modern biological materials do not gather 14C from bomb tests
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the short-lived neutral isotope represented by 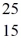 X. Which of the following statements about this isotope are correct? (There may be more than one correct choice.)
X. Which of the following statements about this isotope are correct? (There may be more than one correct choice.)
A) The isotope has 25 nucleons.
B) The isotope has 25 protons.
C) The isotope has 25 neutrons.
D) The isotope has 15 orbital electrons.
E) The isotope has 15 protons.
F) The isotope has 10 neutrons.
H) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a nucleus decays by alpha decay to a daughter nucleus, which of the following statements about this decay are correct? (There may be more than one correct choice.)
A) The daughter nucleus has more protons than the original nucleus.
B) The daughter nucleus has more neutrons than the original nucleus.
C) The daughter nucleus has the same number of nucleons as the original nucleus.
D) The daughter nucleus has fewer protons than the original nucleus.
E) The daughter nucleus has fewer neutrons than the original nucleus.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A radioisotope has a half-life of τ at a temperature of 150 K. If its temperature is increased to 300 K, what will its half-life be?
A) 4τ
B) 2 τ
C) τ
D) τ/2
E) τ/4
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The stability of 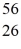 Fe with respect to alpha, β+, and β- decay is to be determined. Do not consider the possibility of decay by electron capture. The following atomic masses are known:
Fe with respect to alpha, β+, and β- decay is to be determined. Do not consider the possibility of decay by electron capture. The following atomic masses are known: 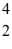 He: 4.002603 u
He: 4.002603 u 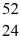 Cr: 51.944768 u
Cr: 51.944768 u 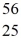 Mn: 55.938907 u
Mn: 55.938907 u 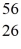 Fe: 55.934939 u
Fe: 55.934939 u 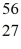 Co: 55.939841 u The
Co: 55.939841 u The  Fe nuclide is
Fe nuclide is
A) not subject to alpha, β+, or β- decay.
B) subject to alpha decay only.
C) subject to β+decay only.
D) subject to β- decay only.
E) subject to β+ or β- decay, but not to alpha decay.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would be the expected radius of a nucleus having 82 protons and 125 neutrons?
A) 5.2 fm
B) 5.9 fm
C) 6.0 fm
D) 7.1 fm
E) 17 fm
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The radioactive nuclei 60Co is widely used in medical applications. It undergoes beta decay, and the total energy of the decay process is 2.82 MeV per decay event. The half-life of this nucleus is 272 days. Suppose that a patient is given a dose of 6.9 µCi of 60Co. If all of this material decayed while in the patient's body, what would be the total energy deposited there? (1 Ci = 3.70 × 1010 decays/s)
A) 11 J
B) 8.6 GJ
C) 3.9 J
D) 24 J
E) 4.15 MJ
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A radioactive isotope decays by β- emission with a half-life of 1.0 min. During the first 1.0 min, a particular sample emits 1000 β- particles. During the next 1.0 min, the number of β- particles this sample will emit will be closest to
A) 250.
B) 500.
C) 1000.
D) 1500.
E) 2000.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The iron nucleus has the greatest binding energy of any nucleus.
A) True
B) False
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A certain nucleus containing 8 protons and 7 neutrons has a radius R. Which of the following values would be closest to the expected value of the radius of a nucleus having 51 protons and 69 neutrons?
A) 1.85R
B) 2.00R
C) 2.14R
D) 6.38R
E) 8.00R
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the strong nuclear force are correct? (There may be more than one correct choice.)
A) It acts equally on protons and neutrons but not on electrons.
B) It acts equally on protons, neutrons, and electrons.
C) It has a much longer range than the electric force.
D) It keeps electrons in their orbits around the nucleus.
E) Because of its very short range, there is a limit to how large the nucleus can be.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the atomic nucleus is correct? (There may be more than one correct choice.)
A) Large nuclei are denser than light nuclei.
B) All nuclei have nearly the same density.
C) The nucleus is held together more by the electrical force than by the gravitational force.
D) A nucleus containing 20 nucleons will have approximately twice the radius as a nucleus containing 10 nucleons.
E) As the number of nucleons increases the binding energy per nucleon always increases.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about β+ decay are correct? (There may be more than one correct choice.) During β+ decay
A) an orbital electron is captured by the nucleus.
B) a proton is emitted from the nucleus.
C) a neutron in the nucleus decays to a proton and an electron.
D) a proton in the nucleus decays to a positron and a neutron.
E) the atomic number Z of the isotope increases by one unit but the atomic weight A remains unchanged.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Radium-226 decays into radon-222 plus an alpha particle. How much energy is released in this process? 1 u = 931.494 MeV/c2, and the relevant mass values are 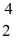 He: 4.002603 u
He: 4.002603 u 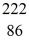 Rn: 222.017570 u
Rn: 222.017570 u 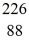 Ra: 226.025402 u
Ra: 226.025402 u
A) 4.24 MeV
B) 3.76 MeV
C) 4.87 MeV
D) 5.05 MeV
E) 5.39 MeV
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the binding energy per nucleon for 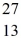 Al? The neutral
Al? The neutral 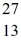 Al atom has a mass of 26.981539 u; a neutral hydrogen atom has a mass of 1.007825 u; a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 u; and a proton has a mass of 1.007277 u. (1 u = 931.494 MeV/c2)
Al atom has a mass of 26.981539 u; a neutral hydrogen atom has a mass of 1.007825 u; a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 u; and a proton has a mass of 1.007277 u. (1 u = 931.494 MeV/c2)
A) 8.3 MeV
B) 6.7 MeV
C) 5.4 MeV
D) 3.4 MeV
E) 2.8 MeV
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The half-life of cobalt-60 is 5.3 years, while that of strontium-90 is 28 years. Suppose that samples of cobalt-60 and strontium-90 are such that they initially have the same activity (number of decays per second) . What is true about the initial numbers of cobalt-60 and strontium-90 nuclei in these samples?
A) There are more strontium-90 than cobalt-60 nuclei.
B) There are equal numbers of cobalt-60 and strontium-90 nuclei.
C) There are more cobalt-60 than strontium-90 nuclei.
D) It is not possible to compare numbers of nuclei without knowing the masses of the samples.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A radioactive atom has 98 protons and 249 nucleons. If it undergoes alpha decay, what are the number of protons and nucleons, respectively, in the daughter nucleus?
A) 100, 245
B) 94, 247
C) 96, 245
D) 96, 247
E) 100, 249
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two identical nuclei of mass 18 u are made to unite to make a single nucleus of mass 36 u. What is the radius of the result of this fusion?
A) 4.0 fm
B) 6.3 fm
C) 4.5 fm
D) 7.2 fm
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The carbon in your body was formed in nuclear reactions in long-dead stars. How much energy was released when three 4He nuclei combined to make 12C? The mass of 4He is 4.002603 u, the mass of 12C is 12.0000 u, and 1 u = 931.494 MeV/c2.
A) 7.274 MeV
B) 3716 MeV
C) 8.424 MeV
D) 2.106 MeV
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 65
Related Exams