A) undergo death as a result of water loss from the cell
B) are unable to metabolize the glucose or fructose, and thus starve to death
C) are obligate anaerobes
D) are unable to swim through these thick and viscous materials
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following observations about flagella is accurate and is consistent with the scientific conclusion that the flagella from eukaryotes and bacteria evolved independently?
A) The flagella of both eukaryotes and bacteria are made of the same protein, but the configuration is different.
B) The mechanics of movement and protein structure are the same in these flagella, but there are significant genetic differences.
C) Although the mechanism of movement in both flagella is the same, the protein that accomplishes the movement is different.
D) The protein structure and the mechanism of movement in eukaryotes flagella are different from those of bacteria flagella.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information and graph to answer the question.
The figure below depicts changes to the amount of DNA present in a recipient cell that is engaged in conjugation with an Hfr cell. Hfr cell DNA begins entering the recipient cell at Time A. Assume that reciprocal crossing over occurs (in other words, a fragment of the recipient's chromosome is exchanged for a homologous fragment from the Hfr cell's DNA) .
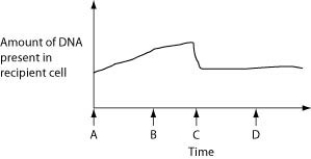 How is the recipient cell different at Time D than it was at Time A?
How is the recipient cell different at Time D than it was at Time A?
A) It has a greater number of genes.
B) It has a greater mass of DNA.
C) It has a different sequence of base pairs.
D) It contains bacteriophage DNA.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Recently, a microbe that is able to digest cellulose was discovered in a hot spring with an average temperature of 95°C. Predict the group to which this microbe most likely belongs.
A) Archaea
B) Proteobacteria
C) Cyanobacteria
D) Fungi
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question refers to the figure.
In this eight-year experiment, 12 populations of E. coli, each begun from a single cell, were grown in low-glucose conditions for 20,000 generations. Each culture was introduced to fresh growth medium every 24 hours. Occasionally, samples were removed from the populations, and their fitness in low-glucose conditions was tested against that of members sampled from the ancestral (common ancestor) E. coli population.
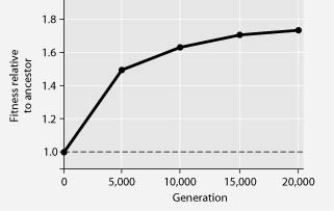 Compare the bacteria in the figure above in generation 1 and generation 20,000. The bacteria in generation 1 have a greater ________.
Compare the bacteria in the figure above in generation 1 and generation 20,000. The bacteria in generation 1 have a greater ________.
A) efficiency at exporting glucose from the cell to the environment
B) ability to survive on simple sugars, other than glucose
C) ability to synthesize glucose from amino acid precursors
D) reliance on glycolytic enzymes
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information and graph to answer the question.
The figure below depicts changes to the amount of DNA present in a recipient cell that is engaged in conjugation with an Hfr cell. Hfr cell DNA begins entering the recipient cell at Time A. Assume that reciprocal crossing over occurs (in other words, a fragment of the recipient's chromosome is exchanged for a homologous fragment from the Hfr cell's DNA) .
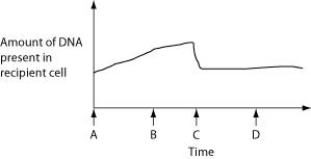 Which two processes are responsible for the shape of the curve at Time B?
Which two processes are responsible for the shape of the curve at Time B?
A) transduction and rolling circle replication of single-stranded Hfr DNA
B) entry of single-stranded Hfr DNA and rolling circle replication of single-stranded Hfr DNA
C) rolling circle replication of single-stranded Hfr DNA and activation of DNA pumps in the plasma membrane
D) transduction and activation of DNA pumps in the plasma membrane
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Genetic variation in bacterial populations cannot result from
A) transduction.
B) conjugation.
C) mutation.
D) meiosis.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a virus infects a bacterial cell, often new viruses are assembled and released when the host bacterial cell is lysed. If these new viruses go on to infect new bacterial cells, the new host cells may not be lysed. What is the most plausible explanation for this?
A) The bacterial cell must be resistant to infection by the virus.
B) The virus carries genes that confer resistance to the host bacterial cell.
C) The host bacterium couples the viral infection with transformation.
D) The virus has entered the genome of the bacterial cell and is in the lysogenic stage.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following table depicts characteristics of five prokaryotic species (A-E) . Use the information in the table to answer the following question.
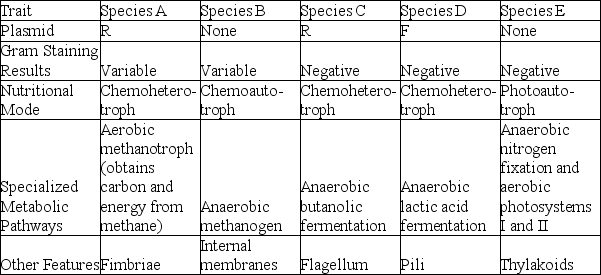 Which two species should have much more phospholipid, in the form of bilayers, in their cytoplasms than most other bacteria?
Which two species should have much more phospholipid, in the form of bilayers, in their cytoplasms than most other bacteria?
A) species A and B
B) species A and C
C) species B and E
D) species C and D
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describe all existing bacteria?
A) pathogenic, omnipresent, morphologically diverse
B) extremophiles, tiny, abundant
C) tiny, ubiquitous, metabolically diverse
D) morphologically diverse, metabolically diverse, extremophiles
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Leaf-cutter ants harvest plant leaves and bring them back to their nests. There, in the warm, moist environments of their underground nests, they grow fungi (Leucoagaricus) that they then eat. These ants also host bacteria on their exoskeleton. Another fungus, Escovopsis, kills Leucoagaricus when the ants are removed from the nest. Knowing that the bacteria on the ants are in the same phylogenetic group of other bacteria that produce antibiotics, which of the following research hypotheses is most likely correct?
A) The bacteria on the exoskeleton produce chemicals that kill Leucoagaricus.
B) The bacteria on the exoskeleton produce chemicals that kill Escovopsis.
C) The bacteria on the exoskeleton provide nutrition to the ants.
D) The bacteria on the exoskeleton cause disease in the ants.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following involves metabolic cooperation among prokaryotic cells?
A) binary fission
B) endospore formation
C) biofilms
D) photoautotrophy
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question refers to the figure.
In this eight-year experiment, 12 populations of E. coli, each begun from a single cell, were grown in low-glucose conditions for 20,000 generations. Each culture was introduced to fresh growth medium every 24 hours. Occasionally, samples were removed from the populations, and their fitness in low-glucose conditions was tested against that of members sampled from the ancestral (common ancestor) E. coli population.
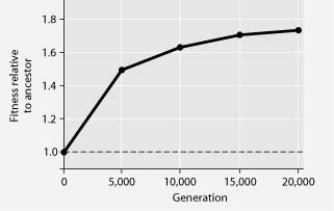 The cells in the 12 cell lines grown in low-glucose conditions showed the effects of which of the following processes?
The cells in the 12 cell lines grown in low-glucose conditions showed the effects of which of the following processes?
A) gene flow and genetic drift
B) natural selection and mutation
C) natural selection and gene flow
D) conjugation and transformation
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Broad-spectrum antibiotics inhibit the growth of most intestinal bacteria. Consequently, assuming that nothing is done to counter the reduction of intestinal bacteria, a hospital patient who is receiving broad-spectrum antibiotics is most likely to become ________.
A) unable to fix carbon dioxide
B) antibiotic resistant
C) unable to synthesize peptidoglycan
D) deficient in certain vitamins and nutrients
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question refers to the figure.
In this eight-year experiment, 12 populations of E. coli, each begun from a single cell, were grown in low-glucose conditions for 20,000 generations. Each culture was introduced to fresh growth medium every 24 hours. Occasionally, samples were removed from the populations, and their fitness in low-glucose conditions was tested against that of members sampled from the ancestral (common ancestor) E. coli population.
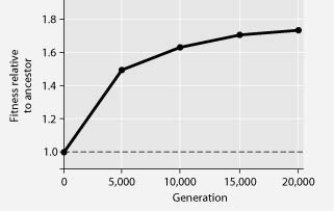 E. coli cells typically make most of their ATP by metabolizing glucose. Under the conditions of this experiment, E. coli generation times in the experimental lines and low-glucose conditions should ________.
E. coli cells typically make most of their ATP by metabolizing glucose. Under the conditions of this experiment, E. coli generation times in the experimental lines and low-glucose conditions should ________.
A) be the same as in the typical environment
B) be faster than in the typical environment
C) be slower than in the typical environment
D) increase over time in the experimental cells
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 75 of 75
Related Exams