A) bipolar spindle formation
B) tethering of chromosomes to microtubules
C) chromosomes dragged to poles by microtubules
D) nuclear envelopes breaking up and reforming
E) none of these
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Meiosis typically results in the production of
A) two diploid cells.
B) four diploid cells.
C) four haploid cells.
D) two haploid cells.
E) one triploid cell.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mature ovum is produced by maturation of the
A) oogonium.
B) primary oocyte.
C) secondary polar body.
D) polar body I.
E) none of these.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chromatids are
A) attached at the centriole.
B) a pair of chromosomes, one from the mother and one from the father.
C) attached at their centromeres.
D) identical until crossing over occurs.
E) attached at their centromeres and are identical until crossing over occurs.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sexual reproduction
A) leads to uniform characteristics within a population.
B) results in new combinations of genetic traits.
C) creates genetic clones.
D) requires less tissue differentiation than asexual reproduction.
E) produces genetic clones and requires less tissue differentiation than asexual reproduction.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following will NOT develop into one or more gametes?
A) spermatogonium
B) polar bodies
C) primary oocyte
D) spermatid
E) secondary spermatocyte
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Paired homologous chromosomes are found at the spindle equator during
A) metaphase I.
B) telophase I.
C) prophase II.
D) metaphase II.
E) anaphase II.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Through meiosis
A) alternate forms of genes are shuffled.
B) parental DNA is divided and distributed to forming gametes.
C) the diploid chromosome number is reduced to haploid.
D) offspring are provided with new gene combinations.
E) all of these occur.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Asexually produced daughter cells are
A) identical to each other.
B) identical to the parental cell.
C) different from the parental cell.
D) different from each other.
E) identical to each other and to the parental cell.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does NOT produce variation?
A) crossing over
B) random alignment of chromosomes during meiosis
C) asexual reproduction
D) genetic recombination of alleles
E) sexual reproduction
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A pine tree is called a sporophyte because it
A) develops from a germinated spore.
B) produces spores by meiosis.
C) is haploid.
D) undergoes fertilization.
E) reproduces by both sexual and asexual means.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If meiosis did NOT occur in sexually reproducing organisms,
A) growth of the zygote would be halted.
B) mitosis would be sufficient.
C) gametes would be haploid.
D) the chromosome number would double in each generation.
E) eggs would be haploid, but sperm would be diploid.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Duplicated chromosomes linked together at their centromeres at the beginning of meiosis are appropriately called what kind of chromatids?
A) mother
B) daughter
C) sister
D) homologous
E) haploid
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Red Queen hypothesis may explain
A) why asexual reproduction is easier and faster than sexual reproduction.
B) why aphids seasonally alternate parthenogenesis with sexual reproduction.
C) the existence of all-female species of animals.
D) the connection between species interactions and sexual reproduction.
E) why meiosis and fertilization alternate during sexual reproduction.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Crossing over
A) generally results in binary fission.
B) involves centrioles.
C) involves breakages and exchanges between sister chromatids.
D) results in new combinations of alleles being channeled into the daughter cells.
E) does all of these.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is TRUE at the end of telophase I in corn (20 chromosomes) ?
A) Each cell has 10 chromosomes.
B) Each chromosome is double-stranded.
C) Centromeres connect sister chromatids.
D) Each cell has 10 chromosomes, and each chromosome is double-stranded.
E) Each cell has 10 chromosomes, each chromosome is double-stranded, and centromeres connect sister chromatids.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The above figure represents 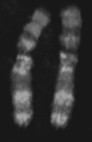
A) individual genes from an asexual worm.
B) maternal chromosomes that are identical.
C) paternal chromosomes that are identical.
D) both maternal and paternal chromosomes.
E) none of these.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sister chromatids are separated from each other during
A) metaphase I.
B) anaphase I.
C) telophase II.
D) anaphase II.
E) metaphase II.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of sexual reproduction?
A) It offers an alternative adaptation in a changing environment.
B) It is adaptive in coevolution situations.
C) It is energetically costly.
D) The genetic variation it provides may be useful in the future.
E) It yields offspring with novel combinations of traits.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following events does NOT occur in prophase II but does occur in prophase I?
A) crossing over
B) pairing of homologues
C) spindle formation
D) crossing over and pairing of homologues only
E) crossing over, pairing of homologues, and spindle formation
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 50
Related Exams