A) glucose
B) proteins
C) fatty acids
D) glucose, proteins, and fatty acids
E) Such yeast cells will not be capable of catabolizing any food molecules, and will therefore die.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9.1 illustrates some of the steps (reactions) of glycolysis in their proper sequence. Each step is lettered. Use these letters to answer the questions.
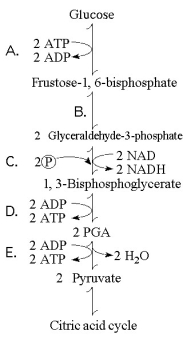 Figure 9.1
-Which step in Figure 9.1 shows a split of one molecule into two smaller molecules?
Figure 9.1
-Which step in Figure 9.1 shows a split of one molecule into two smaller molecules?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the presence of oxygen, the three-carbon compound pyruvate can be catabolized in the citric acid cycle. First, however, the pyruvate (1) loses a carbon, which is given off as a molecule of CO₂, (2) is oxidized to form a two-carbon compound called acetate, and (3) is bonded to coenzyme A. -These three steps result in the formation of
A) acetyl CoA, O₂, and ATP.
B) acetyl CoA, FADH₂, and CO₂.
C) acetyl CoA, FAD, H₂, and CO₂.
D) acetyl CoA, NADH, H⁺, and CO₂.
E) acetyl CoA, NAD⁺, ATP, and CO₂.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration is to
A) yield energy in the form of ATP as it is passed down the respiratory chain.
B) act as an acceptor for electrons and hydrogen, forming water.
C) combine with carbon, forming CO₂.
D) combine with lactate, forming pyruvate.
E) catalyze the reactions of glycolysis.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
High levels of citric acid inhibit the enzyme phosphofructokinase, a key enzyme in glycolysis. Citric acid binds to the enzyme at a different location from the active site. This is an example of
A) competitive inhibition.
B) allosteric regulation.
C) the specificity of enzymes for their substrates.
D) an enzyme requiring a cofactor.
E) positive feedback regulation.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
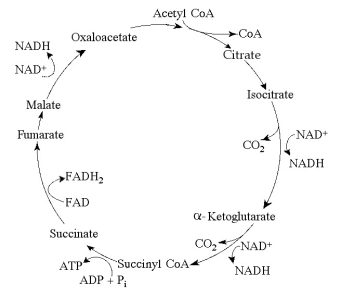 Figure 9.2 The citric acid cycle.
-Starting with citrate, which of the following combinations of products would result from three acetyl CoA molecules entering the citric acid cycle (see Figure 9.2) ?
Figure 9.2 The citric acid cycle.
-Starting with citrate, which of the following combinations of products would result from three acetyl CoA molecules entering the citric acid cycle (see Figure 9.2) ?
A) 1 ATP, 2 CO₂, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH₂
B) 2 ATP, 2 CO₂, 3 NADH, and 3 FADH₂
C) 3 ATP, 3 CO₂, 3 NADH, and 3 FADH₂
D) 3 ATP, 6 CO₂, 9 NADH, and 3 FADH₂
E) 38 ATP, 6 CO₂, 3 NADH, and 12 FADH₂
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 9.1 illustrates some of the steps (reactions) of glycolysis in their proper sequence. Each step is lettered. Use these letters to answer the questions.
 Figure 9.1
-Which step in Figure 9.1 is a redox reaction?
Figure 9.1
-Which step in Figure 9.1 is a redox reaction?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are carbohydrates and fats considered high energy foods?
A) They have a lot of oxygen atoms.
B) They have no nitrogen in their makeup.
C) They can have very long carbon skeletons.
D) They have a lot of electrons associated with hydrogen.
E) They are easily reduced.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An organism is discovered that thrives both in the presence and absence of oxygen in the air. Curiously, the consumption of sugar increases as oxygen is removed from the organism's environment, even though the organism does not gain much weight. This organism
A) must use a molecule other than oxygen to accept electrons from the electron transport chain.
B) is a normal eukaryotic organism.
C) is photosynthetic.
D) is an anaerobic organism.
E) is a facultative anaerobe.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The molecule that functions as the reducing agent (electron donor) in a redox or oxidation-reduction reaction
A) gains electrons and gains potential energy.
B) loses electrons and loses potential energy.
C) gains electrons and loses potential energy.
D) loses electrons and gains potential energy.
E) neither gains nor loses electrons, but gains or loses potential energy.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
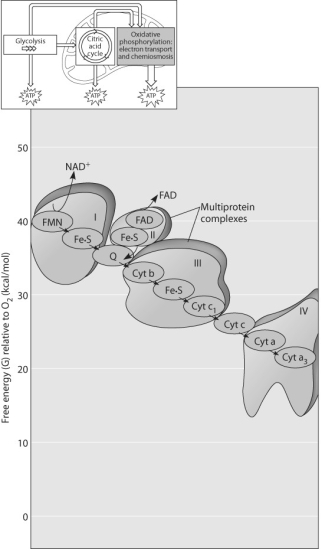 Figure 9.3
-Figure 9.3 shows the electron transport chain. Which of the following is the combination of substances that is initially added to the chain?
Figure 9.3
-Figure 9.3 shows the electron transport chain. Which of the following is the combination of substances that is initially added to the chain?
A) oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water
B) NAD⁺, FAD, and electrons
C) NADH, FADH₂, and protons
D) NADH, FADH₂, and O₂
E) oxygen and protons
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In chemiosmotic phosphorylation, what is the most direct source of energy that is used to convert ADP + 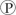 ᵢto ATP?
ᵢto ATP?
A) energy released as electrons flow through the electron transport system
B) energy released from substrate-level phosphorylation
C) energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase, against the electrochemical gradient
D) energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase, down the electrochemical gradient
E) No external source of energy is required because the reaction is exergonic.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 9.3
-Which of the following most accurately describes what is happening along the electron transport chain in Figure 9.3?
Figure 9.3
-Which of the following most accurately describes what is happening along the electron transport chain in Figure 9.3?
A) Chemiosmosis is coupled with electron transfer.
B) Each electron carrier alternates between being reduced and being oxidized.
C) ATP is generated at each step.
D) Energy of the electrons increases at each step.
E) Molecules in the chain give up some of their potential energy.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During intense exercise, as skeletal muscle cells go into anaerobiosis, the human body will increase its catabolism of
A) fats only.
B) carbohydrates only.
C) proteins only.
D) fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
E) fats and proteins only.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements describes the results of this reaction? C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂ → 6 CO₂ + 6 H₂O + Energy
A) C₆H₁₂O₆ is oxidized and O₂ is reduced.
B) O₂ is oxidized and H₂O is reduced.
C) CO₂ is reduced and O₂ is oxidized.
D) C₆H₁₂O₆ is reduced and CO₂ is oxidized.
E) O₂ is reduced and CO₂ is oxidized.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the absence of oxygen, yeast cells can obtain energy by fermentation, resulting in the production of
A) ATP, CO₂, and ethanol (ethyl alcohol) .
B) ATP, CO₂, and lactate.
C) ATP, NADH, and pyruvate.
D) ATP, pyruvate, and oxygen.
E) ATP, pyruvate, and acetyl CoA.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During aerobic respiration, electrons travel downhill in which sequence?
A) food → citric acid cycle → ATP → NAD⁺
B) food → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
C) glucose → pyruvate → ATP → oxygen
D) glucose → ATP → electron transport chain → NADH
E) food → glycolysis → citric acid cycle → NADH → ATP
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many carbon atoms are fed into the citric acid cycle as a result of the oxidation of one molecule of pyruvate?
A) two
B) four
C) six
D) eight
E) ten
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When skeletal muscle cells undergo anaerobic respiration, they become fatigued and painful. This is now known to be caused by
A) buildup of pyruvate.
B) buildup of lactate.
C) increase in sodium ions.
D) increase in potassium ions.
E) increase in ethanol.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is glycolysis described as having an investment phase and a payoff phase?
A) It both splits molecules and assembles molecules.
B) It attaches and detaches phosphate groups.
C) It uses glucose and generates pyruvate.
D) It shifts molecules from cytosol to mitochondrion.
E) It uses stored ATP and then forms a net increase in ATP.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 107
Related Exams