A) pH monitoring.
B) X-ray technology.
C) the diagnosis and treatment of H. pylori infection.
D) colonoscopy.
E) sonography.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Obesity in humans is most clearly linked to
A) type 1 diabetes and prostate cancer.
B) type 1 diabetes and breast cancer.
C) type 2 diabetes and muscle hypertrophy.
D) type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
E) type 2 diabetes and decreased appetite.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ingested dietary substances must cross cell membranes to be used by the body, a process known as
A) ingestion.
B) digestion.
C) hydrolysis.
D) absorption.
E) elimination.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Digestive secretions with a pH of 2 are characteristic of the
A) small intestine.
B) stomach.
C) pancreas.
D) liver.
E) mouth.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In marine sponges, intracellular digestion of peptides is usually immediately preceded by
A) hydrolysis.
B) endocytosis.
C) absorption.
D) elimination.
E) secretion.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following organs is incorrectly paired with its function?
A) stomach-protein digestion
B) oral cavity-starch digestion
C) large intestine-bile production
D) small intestine-nutrient absorption
E) pancreas enzyme production
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
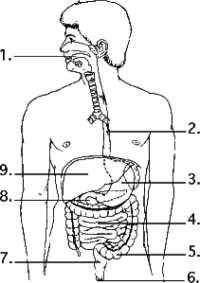 -Examine the digestive system structures in the figure above. Bacteria that produce vitamins as products are residents of location
-Examine the digestive system structures in the figure above. Bacteria that produce vitamins as products are residents of location
A) 3.
B) 4.
C) 5.
D) 7.
E) 8.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you were to jog 1 km a few hours after lunch, which stored fuel would you probably tap?
A) muscle proteins
B) muscle and liver glycogen
C) fat stored in the liver
D) fat stored in adipose tissue
E) blood proteins
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The molar teeth of herbivorous mammals are especially effective at
A) cutting.
B) ripping.
C) grinding.
D) splitting.
E) piercing.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Animals that migrate great distances would obtain the greatest energetic benefit of storing chemical energy as
A) proteins.
B) minerals.
C) carbohydrates.
D) amino acids.
E) fats.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To maintain adequate nutrition, animals require dietary access to certain amino acids. An amino acid that is referred to as "nonessential" would be best described as one that
A) can be made by the animal's body from other substances.
B) is not used by the animal in biosynthesis.
C) must be ingested in the diet.
D) is not readily absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract.
E) is not found in many proteins.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An enzyme with high activity in an acidic environment is
A) amylase.
B) pepsin.
C) gastrin.
D) trypsin.
E) sucrose.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fasting animal whose energy needs exceed those provided in its diet draws on its stored resources in which order?
A) fat, then glycogen, then protein
B) glycogen, then protein, then fat
C) liver glycogen, then muscle glycogen, then fat
D) muscle glycogen, then fat, then liver glycogen
E) fat, then protein, then glycogen
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A nutritional monomer that can be transported in the blood after a typical meal is
A) sucrose.
B) maltose.
C) fatty acid.
D) dipeptide.
E) trinucleotide.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Upon activation by stomach acidity, the secretions of the parietal cells
A) initiate the digestion of protein in the stomach.
B) initiate the mechanical digestion of lipids in the stomach.
C) initiate the chemical digestion of lipids in the stomach.
D) include pepsinogen.
E) delay digestion until the food arrives in the small intestine.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mammalian trachea and esophagus both connect to the
A) large intestine.
B) stomach.
C) pharynx.
D) rectum.
E) epiglottis.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Certain nutrients are considered "essential" in the diets of some animals because
A) only those animals use those nutrients.
B) the nutrients are subunits of important polymers.
C) these animals are not able to synthesize these nutrients.
D) the nutrients are necessary coenzymes.
E) only certain foods contain them.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -Examine the digestive system structures in the figure above. The agents that help emulsify fats are produced in
-Examine the digestive system structures in the figure above. The agents that help emulsify fats are produced in
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 8
E) 9
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A general rule relating the capacity of a specific animal's digestive system to provide adequate access to substrates for biosynthesis of cellular components, as well as fuel molecules needed for ATP production, is that the animal should have access to
A) a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet.
B) a diet low in lipids and high in protein.
C) a low-calorie diet with a large intake of fluids, especially water.
D) a diet that matches the "food pyramid" for the species.
E) a diet that maximizes vitamins and minerals.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A hiatal hernia that disrupts the functional relationship between the smooth muscle in the esophagus and that in the stomach would be most likely to increase the frequency of
A) gastric reflux.
B) premature entry of food into the duodenum.
C) excess secretion of pepsinogen.
D) increased stomach pH.
E) retention of food in the stomach.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 64
Related Exams