A) An increase in wages
B) An increase in the labor force
C) A decrease in net exports
D) A decrease in the personal income tax rates
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An economic analysis of the short run is useful to explain
A) how deviations of real GDP from potential output can and do occur.
B) how deviations of nominal GDP from potential output can and do occur.
C) why the long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical.
D) how an economy's maximum output is determined.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Exhibit: Using the Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model 1 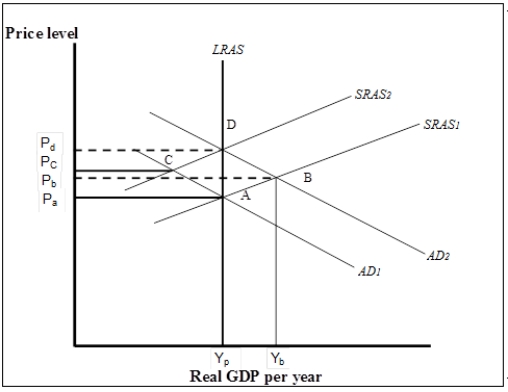 -(Exhibit: Using the Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model 1)
Suppose the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at B.If policy-makers decide to intervene to close the gap, which of the following can it do?
-(Exhibit: Using the Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model 1)
Suppose the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at B.If policy-makers decide to intervene to close the gap, which of the following can it do?
A) Decrease personal income taxes.
B) Increase government welfare spending.
C) Decrease the level of government purchases of goods and services.
D) Institute investment tax credits to encourage business investment.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Exhibit: Aggregate Demand 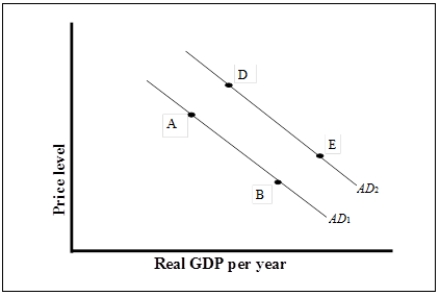 -(Exhibit: Aggregate Demand)
What could have caused the aggregate demand curve to shift to the right from AD1 to AD2?
-(Exhibit: Aggregate Demand)
What could have caused the aggregate demand curve to shift to the right from AD1 to AD2?
A) An increase in exports
B) An increase in imports
C) A decrease in defense spending
D) An increase in the domestic price level
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Exhibit: Long-run Equilibrium 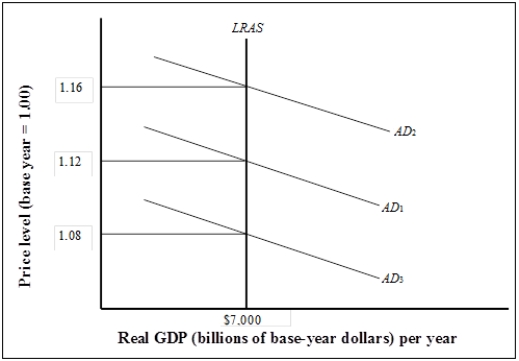 -(Exhibit: Long-run Equilibrium)
If the real GDP is $7,000 billion and the implicit price deflator is 1.08, what is the value of nominal GDP?
-(Exhibit: Long-run Equilibrium)
If the real GDP is $7,000 billion and the implicit price deflator is 1.08, what is the value of nominal GDP?
A) $6,481 billion
B) $7,000 billion
C) $7,560 billion
D) cannot be determined from the information given
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in aggregate demand, all other things unchanged, in the long run will generate
A) an increase in potential output and no change in the price level.
B) a decrease in potential output and no change in the price level.
C) no change in potential output and an increase in the price level.
D) no change in potential output and a decrease in the price level.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model, predict what happens in the short run when there is a general decrease in raw materials cost.
A) The aggregate supply curve shifts right; the aggregate demand curve is not affected; price level decreases; real GDP increases.
B) The aggregate supply curve shifts left; the aggregate demand curve is not affected; price level increases; real GDP decreases.
C) The aggregate demand curve shifts right; the aggregate supply curve is not affected; price level and real GDP increase.
D) The aggregate demand curve shifts left; the aggregate supply curve is not affected; price level and real GDP decrease.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All other things unchanged, an increase in government spending will
A) shift the aggregate demand curve to the right.
B) shift the aggregate demand curve to the left.
C) make the aggregate demand curve flatter.
D) make the aggregate demand curve steeper.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model, predict what happens in the short run when the consumer confidence index falls as consumers become pessimistic about their economic prospects.
A) The aggregate supply curve shifts right; the aggregate demand curve is not affected; price level decreases; real GDP increases.
B) The aggregate supply curve shifts left; the aggregate demand curve is not affected; price level increases; real GDP decreases.
C) The aggregate demand curve shifts right; the aggregate supply curve is not affected; price level and real GDP increase.
D) The aggregate demand curve shifts left; the aggregate supply curve is not affected; price level and real GDP decrease.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Use the following to answer questions
Exhibit: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply at Different Price Levels
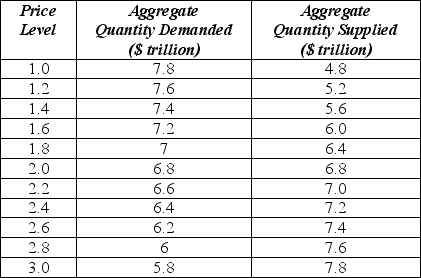 -The aggregate demand curve shifts when the quantity of real GDP demanded at every price level changes.
-The aggregate demand curve shifts when the quantity of real GDP demanded at every price level changes.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Exhibit: Using the Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model 1  -(Exhibit: Using the Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model 1)
Suppose the economy is initially at point A.Now suppose an increase in government purchases shifts the aggregate demand curve to AD2.Which of the following statements best explains how the economy responds to restore long-run macroeconomic equilibrium?
-(Exhibit: Using the Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model 1)
Suppose the economy is initially at point A.Now suppose an increase in government purchases shifts the aggregate demand curve to AD2.Which of the following statements best explains how the economy responds to restore long-run macroeconomic equilibrium?
A) The increase in the price level to Pb reduces real GDP demanded, shifting the aggregate demand curve back to AD1, returning the economy to its potential output at A.
B) Firms produce more in anticipation of future higher prices, thus shifting the SRAS curve upward until the gap is eliminated at D.
C) Firms and workers will negotiate higher nominal wages to restore lost purchasing power.This shifts the SRAS curve to the left until the gap is eliminated at D.
D) The increase in the price level to Pb decreases consumption which in turn leads firms to cut production shifting the SRAS curve to the left until the gap is eliminated at D.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Exhibit: The Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model 1 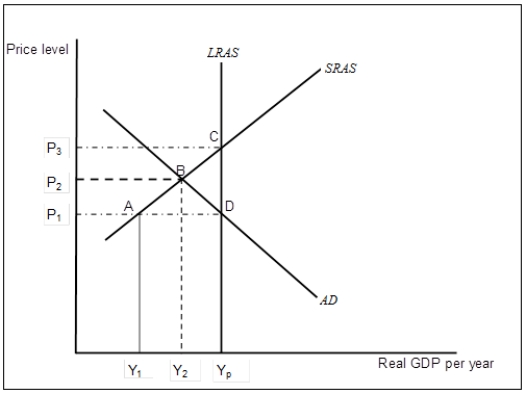 -(Exhibit: The Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model 1)
For the economy represented in the figure,
-(Exhibit: The Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model 1)
For the economy represented in the figure,
A) the real wage rate is higher than full-employment real wage.
B) the real wage rate is lower than full-employment real wage.
C) the nominal wage rate is higher than full-employment nominal wage.
D) the nominal wage rate is lower than full-employment nominal wage.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aggregate demand curve slopes downward I.for the same reasons that an ordinary demand curve does. II.in part because when the price level falls, the real wealth of the public falls, and this induces people to change their consumption. III.because as the price level falls, the net export component of aggregate demand increases.
A) I, II, and III
B) II and III
C) II only
D) III only
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Exhibit: Using the Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model 1  -(Exhibit: Using the Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model 1)
Suppose the economy is initially at point A.All of the following statements are true except
-(Exhibit: Using the Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model 1)
Suppose the economy is initially at point A.All of the following statements are true except
A) the economy is in equilibrium at its potential output.
B) the labor market is in equilibrium.
C) there is no cyclical unemployment.
D) there is no structural or frictional unemployment.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Exhibit: Short-run Aggregate Supply 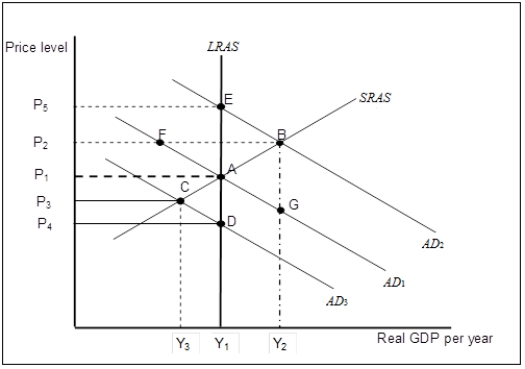 -(Exhibit: Short-run Aggregate Supply)
Suppose that the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A.Now suppose net exports increase.What happens in the short run?
-(Exhibit: Short-run Aggregate Supply)
Suppose that the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A.Now suppose net exports increase.What happens in the short run?
A) There will be an increase in aggregate output demanded and the economy moves from point A to point G.
B) Real GDP increases to Y2 and the price level rises to P2.
C) Real GDP decreases to Y3 and the price level falls to P3.
D) Since the economy is already at its potential output, only the price level will rise to P2.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What happens in the domestic economy when there is a decrease in foreign prices, all other things unchanged?
A) Net exports and aggregate demand fall.
B) Net exports fall and aggregate demand increases.
C) Net exports and aggregate demand increase.
D) Net exports rise and aggregate demand falls.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Exhibit: Long-run Equilibrium  -(Exhibit: Long-run Equilibrium)
If the real GDP is $7,000 billion and the implicit price deflator is 1.16, what is the value of nominal GDP?
-(Exhibit: Long-run Equilibrium)
If the real GDP is $7,000 billion and the implicit price deflator is 1.16, what is the value of nominal GDP?
A) $6,034 billion
B) $8,120 billion
C) $9,120 billion
D) cannot be determined from the information given
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following occurs if an economy experiences a recessionary gap? I.Actual real GDP is less than potential output. II.Actual real GDP is greater than potential output. III.Unemployment is less than the natural rate. IV.Unemployment is greater than the natural rate.
A) I and III
B) I and IV
C) II and III
D) II and IV
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An economy adjusts on its own to close a recessionary gap because there is
A) pressure on nominal wages to fall and this shifts the SRAS curve rightward.
B) pressure on nominal wages to rise and this shifts the SRAS curve rightward.
C) pressure on nominal wages to fall and this shifts the SRAS curve leftward.
D) pressure on nominal wages to rise and this shifts the SRAS curve leftward.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Exhibit: Short-run Aggregate Supply  -(Exhibit: Short-run Aggregate Supply)
Suppose that the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A.Now suppose the stock market crashes, significantly reducing household wealth.What happens in the long-run, all other things unchanged?
-(Exhibit: Short-run Aggregate Supply)
Suppose that the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A.Now suppose the stock market crashes, significantly reducing household wealth.What happens in the long-run, all other things unchanged?
A) The aggregate demand curve will shift back to AD1.
B) The economy will be stuck at an output level below its potential level.
C) The economy returns to full-employment equilibrium at point A.
D) The economy returns to full-employment equilibrium at point D.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 162
Related Exams