A) run test trials with a novel CS
B) run test trials with a novel US
C) change the value of the CS
D) change the value of the US
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Not Answered
Compare general and focal search responses in the sexual behavior system.How does the behavior systems theory account for the different conditional responses that develop as a result of different ISIs in sexual conditioning experiments?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Each of two stimuli fully predicts the presentation of a food pellet when presented alone.When the two stimuli are presented together followed by a food pellet,the associative value
A) of both stimuli increases.
B) of both stimuli decreases.
C) of both stimuli remains the same.
D) of one stimulus decreases while the other decreases.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the behavior systems model,which of the following is true regarding the form of the CR?
A) It will be similar to that of the UR.
B) It will oppose the form of the UR.
C) It will be mediated by the intertrial interval.
D) It will be mediated by the interstimulus interval.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Rescorla-Wagner model assigns the associative value of _____ to a stimulus that is a fully conditioned inhibitor.
A) l
B) 1/2 l
C) 0
D) -l
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increasing CS or US intensity has which of the following effects?
A) speeds associative learning and makes the final level of conditioned responding greater
B) speeds associative learning, but has little effect on the final level of conditioned responding
C) makes the final level of conditioned responding greater, but has little effect on the speed of associative learning
D) has little effect on the speed of associative learning or the final level of conditioned responding
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Higher-order conditioning demonstrates which of the following?
A) After training, a CS can function as a US.
B) After training, a US can function as a CS.
C) CSs cannot function as USs.
D) USs cannot function as CSs.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to Kamin,surprisingness of the US is important in classical conditioning procedures because of which of the following?
A) It stimulates the mental effort needed to form associations.
B) It startles the subject and blocks new learning about stimulus A.
C) It startles the subject and blocks new learning about stimulus B.
D) It startles the subject and blocks new learning about stimulus A and stimulus B.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When live rats were used as the CS in Pavlovian food conditioning trials presented to other,subject rats,the subject rats treated the CS rats in a manner
A) predicted by the stimulus substitution model.
B) predicted by the compensatory-response model.
C) predicted by the US devaluation learning model.
D) not predicted by any of the other answers presented here.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Not Answered
How do current approaches to stimulus substitution differ from Pavlov's approach?
Correct Answer

verified
Answer not provided
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a study with cocaine-using human subjects in the text,which of the following was found to be true?
A) Cues associated with heroin use elicited heart-rate increases and positive changes in mood; cues associated with cocaine use elicited heart rate decreases and positive changes in mood.
B) Cues associated with heroin use elicited heart-rate decreases and positive changes in mood; cues associated with cocaine use elicited heart rate increases and negative changes in mood.
C) Cues associated with heroin use had little effect; cues associated with cocaine use elicited heart rate increases and positive changes in mood.
D) Cues associated with heroin use had little effect; cues associated with cocaine use elicited heart rate increases and negative changes in mood.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using the Rescorla-Wager model,predict 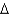 V of stimulus B during conditioning trials with compound stimulus A/B when the associative value of A at the beginning of the trial is l and the associative value of B at the beginning of the trial is l.
V of stimulus B during conditioning trials with compound stimulus A/B when the associative value of A at the beginning of the trial is l and the associative value of B at the beginning of the trial is l.
A) l
B) 1/2 l
C) 0
D) < 0
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the stimulus-substitution model,with training which of the following happens?
A) The CS comes to activate the UR directly.
B) The CR comes to activate the UR directly.
C) The CS activates the UR via excitation of US centers.
D) The CR activates the US via excitation of the UR centers.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From the selection below,select the true statement about stimuli.
A) Identification of CSs and USs is relative.
B) Identification of CSs is relative, but USs do not need reference to other stimuli.
C) Identification of USs is relative, but CSs do not need reference to other stimuli.
D) Identification of CSs and USs does not rely on reference to other stimuli.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the Rescorla-Wagner model,extinction is which of the following?
A) learning a new association
B) imposing an inhibitory stimulus on an excitatory stimulus
C) undoing a conditioned association
D) a process of habituation
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The compensatory-response model challenges the stimulus substitution model because it suggests which of the following?
A) The CR and UR can be the same form and the same strength.
B) The CR and UR can be the same form but not the same strength.
C) The CR and UR can be opposing in form.
D) The CR and UR are unrelated.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the second phase of a blocking experiment,which of the following occurs?
A) Both groups receive the same treatment.
B) The experimental group receives exposure to a compound stimulus; the control group receives exposure to a single stimulus.
C) The experimental group receives exposure to a single stimulus; the control group receives exposure to a compound stimulus.
D) The experimental group receives exposure to a compound stimulus; the control group does not receive any further training.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which model suggests that the CS is only informative if the subject has to wait less time for the US when the CS is present than if it is not present?
A) the Rescorla-Wagner model
B) the Pearce and Hall attentional model
C) the comparator hypothesis
D) the relative-waiting-time hypothesis
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a study with cocaine-using human subjects,cues associated with cocaine use elicited heart rate increases and negative changes in mood.These findings support which of the following?
A) the stimulus substitution model
B) the compensatory-response model
C) the S-R learning model
D) These findings are not consistent with any of the presented models.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to Kamin,the blocking effect occurs because of which choice below?
A) Stimulus B fully predicts the US, and the subject habituates to stimulus A.
B) Stimulus B predicts the US, and the subject is not surprised by the arrival of the US in later trials.
C) Stimulus A predicts the US, and the subject is not surprised by the arrival of the US in later trials.
D) Stimulus A does not predict the US, and the animal is startled by the arrival of the US in later trials.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 68
Related Exams