A) from the demand side.
B) from the supply side.
C) from both the demand and supply side.
D) purely random events.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The proposition that the Fed should concentrate on price stability rather than reducing unemployment is
A) generally accepted by politicians, although few economists accept this proposal.
B) largely accepted by most economists, although politicians do not agree.
C) highly debatable, because many do not agree that price stability should be the most important goal.
D) simply incorrect, and no one accepts this idea anymore.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 17-8
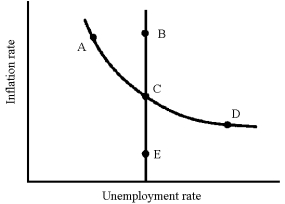 -In Figure 17-8,which of the following movements would you associate with a "negative supply shock"?
-In Figure 17-8,which of the following movements would you associate with a "negative supply shock"?
A) A to B
B) A to C
C) C to E
D) D to E
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A non-policy reason for the reduction in the natural rate of unemployment is the
A) expansionary nature of monetary policy.
B) aging of the U.S. labor force.
C) decline in interest rates.
D) growing federal budget surplus.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Adverse shocks such as the crop failures of 1972-1973 and the oil price increases of 1974 and 1979 pushed the economy's
A) aggregate supply curve outward.
B) Phillips curve inward toward the origin.
C) aggregate supply curve inward.
D) aggregate demand curve inward.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Phillips curve assumes that shocks to the economy come from the demand side.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The aggregate supply curve slopes upward when the real wage falls initially as the price level rises.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If workers always see inflation coming,and if they demand wage increases in advance so that inflation does not erode real wages,then the economy's aggregate supply curve on the AD-AS diagram will
A) be a vertical line corresponding to potential GDP.
B) be a horizontal line corresponding to potential GDP.
C) slope downward.
D) slope upward.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the theory of rational expectations,errors in predicting inflation will
A) be biased upward more often than not.
B) be purely random.
C) tend to be biased downward when inflation is rising, and tend to be biased upward when inflation is falling.
D) tend to be biased upward when inflation is rising, and tend to be biased downward when inflation is falling.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Keynesian view of the world is that the
A) self-correcting mechanism is unreliable.
B) benefits of fighting unemployment are high and the costs are low.
C) short-run Phillips curve is relatively flat.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If aggregate demand in the U.S.had grown more slowly than it actually did in 2010,the
A) unemployment rate would have been even lower.
B) inflation rate would have been even lower.
C) unemployment rate would have been the same.
D) economy would have grown faster.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An economy eliminates a recessionary gap by reducing wages and prices.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the fluctuations in the economy's real growth rate from year to year are caused primarily by variations in the rate at which aggregate supply increases,then data would show
A) a cyclical relationship between inflation and unemployment.
B) a direct relationship between inflation and unemployment.
C) an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment.
D) no relationship between inflation and unemployment.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If nominal wages increase at the same rate as inflation,then the aggregate supply curve will be a horizontal line.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 17-7
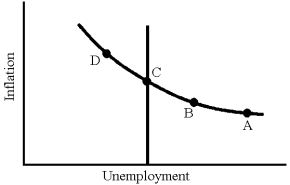 -In Figure 17-7,the case for restrictive monetary and fiscal policy is strongest at point
-In Figure 17-7,the case for restrictive monetary and fiscal policy is strongest at point
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Expansionary fiscal and monetary policy from 2008 to 2010,took the risk of being inflationary for the sake of avoiding additional unemployment.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the theory of rational expectations,the government can influence output
A) with appropriate fiscal and monetary policy.
B) in the short run, but not in the long run.
C) without affecting the price level.
D) only by making unexpected changes in aggregate demand.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the fall of 2007,most economists felt that the
A) unemployment was at the natural rate.
B) unemployment rate was below the natural rate.
C) inflation rate was above the natural rate.
D) inflation rate was below the natural rate.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the aggregate supply curve shifts outward,then unemployment
A) and inflation will both decrease.
B) and inflation will both increase.
C) will increase and inflation will decrease.
D) will decrease and inflation will increase.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Based on the evidence,most economists believe that the self-correcting mechanism operates
A) slowly with prices, but quickly with wages.
B) slowly with wages, but quickly with prices.
C) very slowly with wages.
D) efficiently, so that stabilization policy is not necessary.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 214
Related Exams