A) vaccination
B) denaturation
C) allosteric regulation
D) competitive inhibition
E) feedback inhibition
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which term most precisely describes the cellular process of breaking down large molecules into smaller ones?
A) catalysis
B) metabolism
C) anabolism
D) dehydration
E) catabolism
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true about enzyme-catalyzed reactions?
A) The reaction is faster than the same reaction in the absence of the enzyme.
B) The free energy change of the reaction is opposite from the reaction that occurs in the absence of the enzyme.
C) The reaction always goes in the direction toward chemical equilibrium.
D) Enzyme-catalyzed reactions require energy to activate the enzyme.
E) Enzyme-catalyzed reactions release more free energy than noncatalyzed reactions.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions are based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in the figure below.
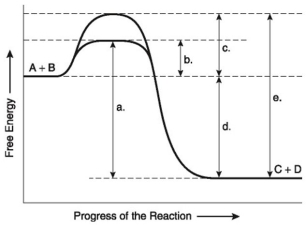 -Which of the following terms best describes the forward reaction in the figure above?
-Which of the following terms best describes the forward reaction in the figure above?
A) endergonic, ∆G > 0
B) exergonic, ∆G < 0
C) endergonic, ∆G < 0
D) exergonic, ∆G > 0
E) chemical equilibrium, ∆G = 0
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. Succinate dehydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of succinate to fumarate.The reaction is inhibited by malonic acid,which resembles succinate but cannot be acted upon by succinate dehydrogenase.Increasing the ratio of succinate to malonic acid reduces the inhibitory effect of malonic acid. -What is malonic acid's role with respect to succinate dehydrogenase?
A) It is a competitive inhibitor.
B) It blocks the binding of fumarate.
C) It is a noncompetitive inhibitor.
D) It is able to bind to succinate.
E) It is an allosteric regulator.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true for all exergonic reactions?
A) The products have more total energy than the reactants.
B) The reaction proceeds with a net release of free energy.
C) The reaction goes only in a forward direction: all reactants will be converted to products, but no products will be converted to reactants.
D) A net input of energy from the surroundings is required for the reactions to proceed.
E) The reactions are rapid.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In experimental tests of enzyme evolution,in which a gene encoding an enzyme is subjected to multiple cycles of random mutagenesis and selection for altered substrate specificity,the resulting enzyme had multiple amino acid changes associated with altered substrate specificity.Where in the enzyme were these amino acid changes located?
A) only in the active site
B) only in the active site or near the active site
C) in or near the active site and at surface sites away from the active site
D) only at surface sites away from the active site
E) only in the hydrophobic interior of the folded protein
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A number of systems for pumping ions across membranes are powered by ATP.Such ATP-powered pumps are often called ATPases although they don't often hydrolyze ATP unless they are simultaneously transporting ions.Because small increases in calcium ions in the cytosol can trigger a number of different intracellular reactions,cells keep the cytosolic calcium concentration quite low under normal conditions,using ATP-powered calcium pumps.For example,muscle cells transport calcium from the cytosol into the membranous system called the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) .If a resting muscle cell's cytosol has a free calcium ion concentration of 10⁻⁷ while the concentration in the SR is 10⁻²,then how is the ATPase acting?
A) ATPase activity must be powering an inflow of calcium from the outside of the cell into the SR.
B) ATPase activity must be transferring℗ ᵢ to the SR to enable this to occur.
C) ATPase activity must be pumping calcium from the cytosol to the SR against the concentration gradient.
D) ATPase activity must be opening a channel for the calcium ions to diffuse back into the SR along the concentration gradient.
E) ATPase activity must be routing calcium ions from the SR to the cytosol, and then to the cell's environment.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + ℗ᵢ,the free energy change is -7.3 kcal/mol under standard conditions (1 M concentration of both reactants and products) .In the cellular environment,however,the free energy change is about -13 kcal/mol.What can we conclude about the free energy change for the formation of ATP from ADP and℗ ᵢ under cellular conditions?
A) It is +7.3 kcal/mol.
B) It is less than +7.3 kcal/mol.
C) It is about +13 kcal/mol.
D) It is greater than +13 kcal/mol.
E) The information given is insufficient to deduce the free energy change.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following shows the correct changes in thermodynamic properties for a chemical reaction in which amino acids are linked to form a protein?
A) +ΔH, +ΔS, +ΔG
B) +ΔH, -ΔS, -ΔG
C) +ΔH, -ΔS, +ΔG
D) -ΔH, -ΔS, +ΔG
E) -ΔH, +ΔS, +ΔG
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the question below.
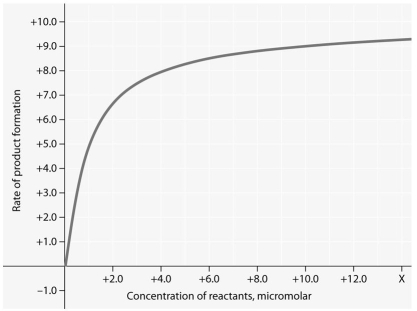 Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying reactant
concentration,with the concentration of enzyme constant.
-For the enzyme-catalyzed reaction shown in the figure,which of these treatments will cause the greatest increase in the rate of the reaction,micromolar?
Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying reactant
concentration,with the concentration of enzyme constant.
-For the enzyme-catalyzed reaction shown in the figure,which of these treatments will cause the greatest increase in the rate of the reaction,micromolar?
A) doubling the activation energy needed
B) cooling the reaction by 10°C
C) doubling the concentration of the reactants from 1.0 to 2.0 micromolar
D) tripling the concentration of the reactants from 1.0 to 3.0 micromolar
E) reducing the ΔG
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Energy coupling occurs when
A) an endergonic reaction drives an exergonic reaction.
B) an exergonic reaction drives an endergonic reaction.
C) heat is generated.
D) allosteric interactions are at work.
E) chemical equilibrium is reached.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 92 of 92
Related Exams