A) telophase
B) anaphase
C) prometaphase
D) metaphase
E) prophase
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Proteins that are involved in the regulation of the cell cycle,and that show fluctuations in concentration during the cell cycle,are called
A) ATPases.
B) kinetochores.
C) kinases.
D) proton pumps.
E) cyclins.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are primarily responsible for cytokinesis in plant cells but not in animal cells?
A) kinetochores
B) Golgi-derived vesicles
C) actin and myosin
D) centrioles and centromeres
E) cyclin-dependent kinases
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Besides the ability of some cancer cells to overproliferate,what else could logically result in a tumour?
A) metastasis
B) changes in the order of cell cycle stages
C) lack of appropriate cell death
D) inability to form spindles
E) inability of chromosomes to meet at the metaphase plate
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a protein maintained at constant levels throughout the cell cycle that requires cyclin to become catalytically active?
A) PDGF
B) MPF
C) protein kinase
D) cyclin
E) Cdk
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. You observe cells under the microscope and notice that,while in telophase,small vesicles line up along the middle of the cell. -The event that you are witnessing is
A) cytokinesis.
B) cleavage.
C) meiosis.
D) apoptosis.
E) binary fission.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cells from an advanced malignant tumour most often have very abnormal chromosomes,and often an abnormal total number of chromosomes.Why might this occur?
A) Cancer cells are no longer density dependent.
B) Cancer cells are no longer anchorage dependent.
C) Chromosomally abnormal cells can still go through cell cycle checkpoints.
D) Chromosomally abnormal cells still have normal metabolism.
E) Transformation introduces new chromosomes into cells.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus.How many picograms would be found at the end of S and the end of G₂?
A) 8; 8
B) 8; 16
C) 16; 8
D) 16; 16
E) 12; 16
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following information applies to the questions below. Several organisms,primarily protists,have what are called intermediate mitotic organization. -These protists are intermediate in what sense?
A) They reproduce by binary fission in their early stages of development and by mitosis when they are mature.
B) They never coil up their chromosomes when they are dividing.
C) They use mitotic division but only have circular chromosomes.
D) They maintain a nuclear envelope during division.
E) None of them form spindles.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One difference between cancer cells and normal cells is that cancer cells
A) are unable to synthesize DNA.
B) are arrested at the S phase of the cell cycle.
C) continue to divide even when they are tightly packed together.
D) cannot function properly because they are affected by density-dependent inhibition.
E) are always in the M phase of the cell cycle.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a newly evolving protist,what would be the advantage of using eukaryote-like cell division rather than prokaryotic binary fission?
A) Binary fission would not allow for the formation of new organisms.
B) Cell division would allow for the orderly and efficient segregation of multiple linear chromosomes.
C) Cell division would be faster than binary fission.
D) Cell division allows for lower rates of error per chromosome replication.
E) Binary fission would not allow the organism to have complex cells.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How do kinetochore microtubules assist in the process of splitting centromeres?
A) using motor proteins to split the centromere at specific arginine residues
B) creating tension by pulling toward opposite poles
C) sliding past each other like actin filaments
D) phosphorylating the centromere, thereby changing its conformation
E) attach the centromere to the nuclear envelope
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions are based on the following figure.
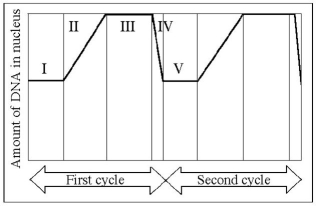 -At which of the numbered regions would you expect to find cells at metaphase?
-At which of the numbered regions would you expect to find cells at metaphase?
A) I and IV
B) II only
C) III only
D) IV only
E) V only
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does disappearance of the nuclear envelope permit in human and many other eukaryotic cells?
A) cytokinesis
B) the attachment of microtubules to kinetochores
C) the splitting of the centrosomes
D) the disassembly of the nucleolus
E) replication of DNA
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a biologist can separate one of a dozen pieces of chromatin from a eukaryotic (animal) nucleus.It might consist of which of the following?
A) one-twelfth of the genes of the organism
B) two chromosomes, each with six chromatids
C) a single circular piece of DNA
D) two long strands of DNA plus proteins
E) two chromatids attached together at a centromere
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where do the microtubules of the spindle originate during mitosis in both plant and animal cells?
A) centromere
B) centrosome
C) centriole
D) chromatid
E) kinetochore
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do neurons and some other specialized cells divide infrequently?
A) They no longer have active nuclei.
B) They no longer carry receptors for signal molecules.
C) They have been shunted into G₀.
D) They can no longer bind Cdk to cyclin.
E) They show a drop in MPF concentration.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What happens in G₁?
A) normal growth and cell function
B) DNA replication
C) mitosis
D) senescence
E) cell division
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 98 of 98
Related Exams