A) pore cells.
B) epidermal cells.
C) choanocytes.
D) amoebocytes.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following combinations correctly matches a phylum to its description?
A) Echinodermata - bilateral symmetry as a larva, water vascular system
B) Nematoda - segmented worms, closed circulatory system
C) Cnidaria - flatworms, gastrovascular cavity, acoelomate
D) Platyhelminthes - radial symmetry, polyp and medusa body forms
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You find a small animal with eight legs crawling up your bedroom wall.Closer examination will probably reveal that this animal has
A) simple, but not compound, eyes.
B) two pairs of antennae.
C) a head, thorax, and abdomen.
D) tracheae and spiracles.
E) more than one of these.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
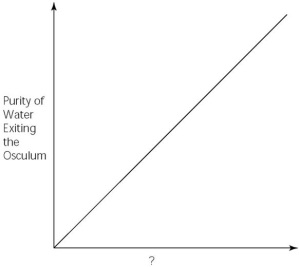 -Which of the following factors,when used to label the horizontal axis of the above graph,would account most directly for the shape of the plot?
-Which of the following factors,when used to label the horizontal axis of the above graph,would account most directly for the shape of the plot?
A) spongin concentration (gm/unit volume)
B) rate of cribrostatin synthesis (molecules/unit time)
C) number of pores per sponge
D) number of spicules per sponge
E) number of choanocytes per sponge
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a major disadvantage of exoskeletons?
A) Exoskeletons can be easily punctured.
B) An exoskeleton provides some support.
C) An exoskeleton grows faster than the animal.
D) An exoskeleton does not grow as the animal grows.
E) An exoskeleton tastes good to predators.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Humans most frequently acquire trichinosis by
A) having sexual contact with an infected partner.
B) eating undercooked pork.
C) inhaling the eggs of worms.
D) eating undercooked beef.
E) being bitten by tsetse flies.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which chemical is synthesized by some sponges and acts as an antibiotic?
A) streptomycin
B) spongin
C) calcium carbonate
D) silica
E) cribrostatin
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. A farm pond,usually dry during winter,has plenty of water and aquatic pond life during the summer.One summer,Sarah returns to the family farm from university.Observing the pond,she is fascinated by some six-legged organisms that can crawl about on submerged surfaces or,when disturbed,seemingly "jet" through the water.Watching further,she is able to conclude that the "mystery organisms" are ambush predators,and their prey includes everything from insects to small fish and tadpoles. -Sarah noticed the presence of many empty exoskeletons attached to emergent vegetation.These exoskeletons looked exactly like those of the largest of the "mystery organism" she had seen in the pond.They also looked similar to the bodies of the dragonflies that patrolled the surface of the pond.If Sarah had learned a lot from her biology class,what should she have concluded about the mysterious pond organisms?
A) They are larval dragonflies, destined to undergo incomplete metamorphosis.
B) They are larval dragonflies, destined to undergo complete metamorphosis.
C) They are adult dragonflies, so old that they can no longer fly, have fallen into the pond, but have not yet drowned.
D) They are adult dragonflies that must, like many amphibian species, return to water in order to mate.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The great success of insects on land can be attributed to which key adaptation?
A) the ability to fly
B) jointed appendages allowing quick movement
C) the ability to undergo metamorphosis
D) large variation in different kinds of appendages
E) the ability to eat both plants and animals
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which clade in the phylum Cnidaria includes "jellies" with rounded (as opposed to boxlike) medusae?
A) Hydrozoa
B) Scyphozoa
C) Anthozoa
D) Cubozoa
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a characteristic of nematodes?
A) All species can be characterized as scavengers.
B) They have only longitudinal muscles.
C) They have a true coelom.
D) They have a gastrovascular cavity.
E) Many species are diploblastic.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which characteristic(s) is (are) shared by both cnidarians and flatworms?
A) dorsoventrally flattened bodies
B) true muscle
C) radial symmetry
D) a digestive system with a single opening
E) two of these
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The teacher was unaware of the difference between suspension feeding and predation.The teacher thought that providing live copepods (2 mm long) and feeder fish (2 cm long) would satisfy the dietary needs of all of the organisms.Consequently,which two organisms would have been among the first to starve to death (assuming they lack photosynthetic endosymbionts) ?
A) sponges and corals
B) sea stars and sponges
C) shrimp and bivalves
D) corals and bivalves
E) bivalves and sponges
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The teacher and class were especially saddened when the colonial hydrozoan died.They had watched it carefully,and the unfortunate creature never even got to produce offspring by budding.Yet,everyone was elated when Tommy (now recovered) noticed a small colonial hydrozoan growing in a part of the tank far from the location of the original colony.The teacher was apparently unaware that these hydrozoans exhibit
A) spontaneous generation.
B) abiogenesis.
C) alternation of generations.
D) ecdysis.
E) a medusa stage.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One should expect to find the "9 + 2 pattern" of microtubules in association with the feeding apparatus of which of the following?
A) annelids
B) coral animals
C) tapeworms
D) sponges
E) terrestrial insects
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nematocysts of sea slugs should be most effective at protecting individual sea slugs from predation if the predators
A) remove small bites of flesh from sea slugs, and have long-term memory.
B) remove small bites of flesh from sea slugs, and have no long-term memory.
C) consume entire sea slugs in one gulp, and have no long-term memory.
D) consume entire sea slugs in one gulp, and have long-term memory.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You find what you believe is a new species of animal.Which of the following characteristics would enable you to argue that it is more closely related to a flatworm than it is to a roundworm?
A) It is a suspension feeder.
B) It has no coelom.
C) It is shaped like a worm.
D) It has a mouth and an anus.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
While sampling marine plankton in a lab,a student encounters large numbers of fertilized eggs.The student rears some of the eggs in the laboratory for further study and finds that the blastopore becomes the mouth.The embryo develops into a trochophore larva and eventually has a true coelom.These eggs probably belonged to a(n)
A) chordate.
B) echinoderm.
C) mollusc.
D) nematode.
E) arthropod.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Among the invertebrate phyla,phylum Arthropoda is unique in possessing members that have
A) a cuticle.
B) a ventral nerve cord.
C) open circulation.
D) wings.
E) segmented bodies.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The heartworms that can accumulate within the hearts of dogs and other mammals have a pseudocoelom,an alimentary canal,and an outer covering that is occasionally shed.To which phylum does the heartworm belong?
A) Platyhelminthes
B) Arthropoda
C) Nematoda
D) Acoela
E) Annelida
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 111
Related Exams