A) 1
B) 1 and 2
C) 2 and 3
D) 3
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Adrenergic synapses release the neurotransmitter
A) acetylcholine.
B) norepinephrine.
C) dopamine.
D) serotonin.
E) GABA.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following would the rate of impulse conduction be the greatest?
A) a myelinated fiber of 10-µm diameter
B) a nonmyelinated fiber of 20-µm diameter
C) a myelinated fiber of 1-µm diameter
D) a nonmyelinated fiber of 10-µm diameter
E) It would be the same in all because of the all-or-none principle.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most neurons lack ________ and so are permanently blocked from undergoing cell division.
A) ribosomes
B) endoplasmic reticula
C) a nucleus
D) centrioles
E) cytoplasm
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How would a chemical that prevents the opening of voltage-regulated Na+ channels affect the function ofa neuron?
A) The neuron will only be able to hyperpolarize.
B) The neuron will depolarize more rapidly.
C) Action potentials will lack a repolarization phase.
D) The neuron will automatically and repeatedly produce graded potentials.
E) The neuron will only be capable of producing graded potentials.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 12-2 The Nerve Action Potential
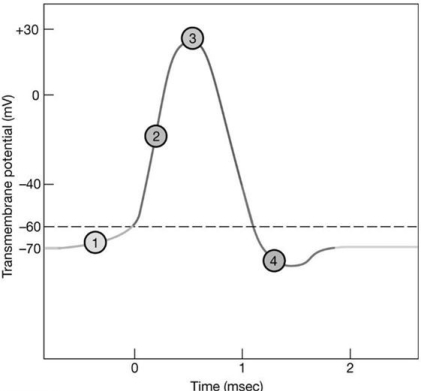 Use Figure 12-2 to answer the following questions:
-Which area of the graph shows when potassium channels open?
Use Figure 12-2 to answer the following questions:
-Which area of the graph shows when potassium channels open?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following activities or sensations is/are not monitored by interoceptors?
A) sight
B) pain
C) activities of the digestive system
D) cardiovascular activities
E) urinary activities
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which neurotransmitter has widespread effects on a person's attention and emotional state?
A) dopamine
B) norepinephrine
C) serotonin
D) GABA
E) endorphins
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ nerves are nerves that connect to the spinal cord.
A) Spinal
B) Cranial
C) Afferent
D) Multipolar
E) Autonomic
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following can cause demyelination?
A) arsenic poisoning
B) diphtheria
C) multiple sclerosis
D) mercury exposure
E) Demyelination can be caused by arsenic, diphtheria, multiple sclerosis and mercury.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ carry motor information to peripheral effectors.
A) Unipolar neurons
B) Efferent neurons
C) Multipolar neurons
D) Afferent neurons
E) Interneurons
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The molecule responsible for making cyclic AMP is called
A) adenylate cyclase.
B) adenosine.
C) anandamide.
D) adenosine synthase.
E) G-protein.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Opening of sodium channels in the axon membrane causes
A) depolarization.
B) repolarization.
C) hyperpolarization.
D) increased negative charge inside the membrane.
E) inhibition.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Damage to ependymal cells would most likely affect the
A) formation of myelin sheaths.
B) formation of cerebrospinal fluid.
C) formation of ganglia.
D) repair of axons.
E) transport of neurotransmitters within axons.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The neuroglial cells that participate in maintaining the blood-brain barrier are the
A) astrocytes.
B) ependymal cells.
C) microglia.
D) oligodendrocytes.
E) Schwann cells.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When potassium channels open and the ions diffuse through the membrane,
A) the inside of the membrane will become more positive.
B) the inside of the membrane will become more negative.
C) there will be almost no effect on transmembrane potential.
D) the membrane will become depolarized.
E) the membrane will depolarize to threshold.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Below are the events that occur during continuous propagation of action potential. Select the correct order in which the events occur. 1) Adjacent membrane segment depolarizes. 2) Local current spreads to adjacent voltage gated channel. 3) Threshold is met. 4) Local current develops due to sodium moving in the cytosol.
A) 2,4,3,1
B) 2,4,1,3
C) 4,2,3,1
D) 4,2,1,3
E) 1,4,2,3
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ channels open or close in response to physical distortion of the membrane surface.
A) Voltage-gated
B) Chemically gated
C) Active
D) Mechanically gated
E) Leak
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The axon is connected to the soma at the
A) telodendria.
B) synaptic terminal.
C) collaterals.
D) axon hillock.
E) synapse.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 12-2 The Nerve Action Potential
 Use Figure 12-2 to answer the following questions:
-Which area of the graph shows when voltage-gated sodium channels are open?
Use Figure 12-2 to answer the following questions:
-Which area of the graph shows when voltage-gated sodium channels are open?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 1
D) 5
E) 3
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 158
Related Exams