A) 1
B) 3
C) 6
D) 9
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mode of ventilation that maintains a minimum VE by increasing or decreasing the amount of support (VT or respiratory rate) given to the patient is ___________________.
A) volume support
B) automatic tube compensation
C) mandatory minute ventilation
D) adaptive support ventilation
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which mode of ventilation delivers the exact amount of pressure required to overcome the resistive load imposed by the ET tube for the flow measured at the time?
A) Automode
B) Volume-targeted PSV
C) Pressure support ventilation
D) Automatic tube compensation
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a patient who has failed an SBT still meets the criteria for discontinuation of ventilation,an SBT should be performed every _______ hours to determine weanability.
A) 6
B) 12
C) 24
D) 36
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At what pressure is pressure support not high enough to contribute significantly to ventilatory support but is sufficient to overcome the work imposed by the ventilator system?
A) 2 cm H2O
B) 5 cm H2O
C) 8 cm H2O
D) 10 cm H2O
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sixty minutes after a patient is extubated,an arterial blood gas sample is drawn;the results are: pH = 7.20,PaCO2 = 60 mm Hg,PaO2 = 55 mm Hg,SaO2 = 80%,HCO3- = 23 mEq/L with a 2 L/min nasal cannula.The patient is SOB and complaining of chest pain.His blood pressure is 92/50 mm Hg.The most likely cause of this weaning failure is which of the following?
A) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
B) Acute left ventricular failure
C) Ventilatory muscle weakness
D) Hypophosphatemia
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which parameter is used as the primary index of the drive to breathe?
A) Airway occlusion pressure
B) CROP index
C) Maximum inspiratory pressure
D) Rapid shallow breathing index
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A recently extubated patient develops a partial upper airway obstruction,which causes stridor.What action can the respiratory therapist take to improve the patient's condition?
A) Aerosolize 11.25 mg of racemic epinephrine.
B) Put a nonrebreathing mask on the patient.
C) Place the patient on NPPV.
D) Suggest the use of lorazepam (Ativan) .
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How long does a tracheostomy site typically take to mature?
A) 2 to 4 days
B) 4 to 6 days
C) 7 to 12 days
D) 10 to 15 days
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A postoperative patient,still under anesthesia,is being ventilated with VC-CMV with Automode.After 2 hours the patient is waking up and beginning to breathe spontaneously.The ventilator will respond by _____________________.
A) switching to the pressure support mode.
B) switching to the volume support mode.
C) delivering time-triggered,pressure-limited breaths.
D) ensuring minimum mandatory minute ventilation.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which patient would continued use of an artificial airway be necessary?
A) A patient with upper airway burns and no peritubular leak
B) A patient who tests positive for a peritubular leak
C) A patient with bronchospasm and supplemental oxygen requirements
D) A patient with a strong cough who expectorates moderate amounts of sputum
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 46-year-old male patient (IBW = 85 kg) who was injured in a motor vehicle accident has been receiving invasive mechanical ventilation for 24 hours.The patient is awake and alert and looks comfortable on these settings: VC-SIMV with pressure support of 5 cm H2O;set rate = 8 breaths/min;set VT = 500 mL;FIO2 = 0.4;PEEP = 5 cm H2O.A 10-minute spontaneous breathing trial (SBT) yields this information: f = 30 breaths/min,RSBI = 145,P0.1 = 10 cm H2O.What should the respiratory therapist suggest to the physician during patient rounds?
A) Sedate the patient and place him on VC-CMV.
B) Continue with the current ventilator settings.
C) Switch to PC-CMV with a rate of 14 breaths/min.
D) Decrease the mandatory SIMV rate to 4 breaths/min.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient being actively weaned from mechanical ventilation currently is receiving the following ventilatory support: pressure support = 15 cm H2O,spontaneous VT = 575 mL,spontaneous rate = 14 breaths/min,spontaneous VT = 500 mL,FIO2 = 35%,PEEP = 5 cm H2O.The arterial blood gas results are: pH = 7.42,PaCO2 = 38 mm Hg,PaO2 = 94 mm Hg,SaO2 = 98%,HCO3- = 24 mEq/L.What should the respiratory therapist do next?
A) Reduce PEEP to zero.
B) Reduce the FIO2 to 30%.
C) Reduce the PS to 10 cm H2O.
D) Extubate the patient.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assess the following data obtained from the spontaneous breathing trials of four patients.Which patient is most likely to be weaned successfully at this time?
A) Spontaneous rate = 32 breaths/min,VT = 375 mL,PaO2 = 98 mm Hg,FIO2 = 0.4
B) Spontaneous rate = 15 breaths/min,VT = 450 mL,PaO2 = 87 mm Hg,FIO2 = 0.6
C) Spontaneous rate = 15 breaths/min,VT = 650 mL,PaO2 = 91 mm Hg,FIO2 = 0.28
D) Spontaneous rate = 12 breaths/min,VT = 680 mL,PaO2 = 79 mm Hg,FIO2 = 0.5
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An SBT should not continue for longer than _____ minutes.
A) 30
B) 60
C) 120
D) 180
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient is extubated and placed on a cool,bland aerosol with 30% oxygen.Twenty minutes postextubation,the respiratory therapist is called to assess the patient,who has shortness of breath.The respiratory therapist observes intercostal retractions,accessory muscle use,and a respiratory rate of 38 breaths/min.Stridor can be heard without a stethoscope,and the SpO2 has dropped from 97% to 85%.The patient is given an aerosolized racemic epinephrine treatment and reassessed.Accessory muscle use continues,intercostal retractions decrease slightly,and stridor is heard on auscultation.The patient's respiratory rate is 30 breaths/min,and the SpO2 is 88%.What should the respiratory therapist recommend?
A) Reintubation and mechanical ventilation
B) Heliox therapy and steroid administration
C) Increase the FIO2 on the cool bland aerosol to 40%
D) Use a nonrebreather mask with 15 L/min oxygen
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What ends inspiration in pressure support ventilation?
A) Time
B) Flow
C) Volume
D) Pressure
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ACCP/SCCM/AARC task force recommends that a search for all possible causes that may be contributing to ventilator dependence be undertaken in patients who require mechanical ventilation for longer than ______ hours.
A) 12
B) 24
C) 48
D) 72
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient is being weaned from invasive mechanical ventilation using VC-SIMV without pressure support.The respiratory therapist reviews the following data from the last few hours. 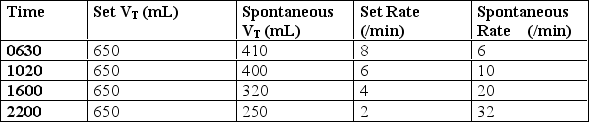 What should the respiratory therapist recommend for this patient?
What should the respiratory therapist recommend for this patient?
A) Switch the mode to VC-CMV.
B) Add and titrate pressure support.
C) Extubate and place the patient on NPPV.
D) Increase the set rate to 8 breaths/min.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The closed loop mode used for weaning from mechanical ventilation is which of the following?
A) Pressure support ventilation
B) Adaptive support ventilation
C) Continuous positive airway pressure
D) Intermittent mandatory ventilation
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 23
Related Exams