A) Astrocyte
B) Ependymal cell
C) Neurolemmocyte
D) Microglial cell
E) Oligodendrocyte
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A secondary tumor is one that originates in one site but subsequently spreads to another site.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The function of neurofibril nodes is to
A) inhibit the transmission of a nerve impulse.
B) provide points of attachment for nerve threads.
C) produce a faster nerve impulse through salutatory conduction.
D) produce a slower impulse through continuous conduction.
E) protect the delicate axon sheath.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not one of the three common structural types of synapses?
A) Axonucleic
B) Axoaxonic
C) Axosomatic
D) Axodendritic
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of the two types of synapses,based on mode of communication,which is slower and more common?
A) Chemical synapse
B) Mechanical synapse
C) Physical synapse
D) Magnetic synapse
E) Electrical synapse
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The part of the neuron responsible for receiving,integrating,and sending nerve impulses is the
A) dendrite.
B) axon.
C) cell body.
D) axon hillock.
E) telodendrion.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What cell type does number 2 indicate? 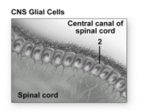
A) Satellite cell
B) Neuron
C) Microglial cell
D) Astrocyte
E) Ependymal cell
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Glial cells differ from neurons in that they
A) are larger and capable of meiosis.
B) are smaller and capable of mitosis.
C) are found only in the CNS.
D) are found only in the PNS.
E) transmit nerve impulses much more slowly.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where are synaptic knobs located?
A) At the tips of telodendria
B) At the ends of dendrites
C) Within the cell body
D) Along axon collaterals
E) At the axon hillock
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Based on function,99 percent of neurons are
A) sensory neurons.
B) motor neurons.
C) multipolar neurons.
D) bipolar neurons.
E) interneurons.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Continuous conduction of a nerve impulse occurs only along
A) myelinated axons.
B) dendrites.
C) unmyelinated axons.
D) axons in the PNS.
E) axons in the CNS.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The nervous system serves a major role in body movement by controlling receptors that cause skeletal muscle to contract.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are two types of synapses,based on mode of communication.What are they?
A) Mechanical and chemical
B) Magnetic and physical
C) Physical and chemical
D) Chemical and electrical
E) Mechanical and electrical
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 93 of 93
Related Exams