A) consumers are now willing to purchase more of this product at each possible price.
B) the product has become particularly scarce for some reason.
C) product price has fallen and as a consequence consumers are buying a larger quantity of the product.
D) the demand curve has shifted to the left.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the following question you are asked to determine,other things equal,the effects of a given change in a determinant of demand or supply for product X upon (1) the demand (D) for,or supply (S) of,X; (2) the equilibrium price (P) of X;and (3) the equilibrium quantity (Q) of X. An increase in the price of a product that is a complement to X will:
A) decrease S,decrease P,and decrease Q.
B) decrease D,decrease P,and decrease Q.
C) increase D,increase P,and increase Q.
D) increase D,increase P,and decrease Q.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In constructing a stable demand curve for product X:
A) consumer preferences are allowed to vary.
B) the prices of other goods are assumed constant.
C) money incomes are allowed to vary.
D) the supply curve of product X is assumed to be fixed.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
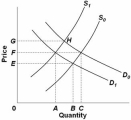 Refer to the above diagram,which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for product X.If supply is S1 and demand D0,then:
Refer to the above diagram,which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for product X.If supply is S1 and demand D0,then:
A) at any price above 0G a shortage would occur.
B) 0F represents a price that would result in a surplus of AC.
C) a surplus of GH would occur.
D) 0F represents a price that would result in a shortage of AC.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A binding price ceiling means that:
A) there is currently a surplus of the relevant product.
B) government is imposing a legal price that is typically below the equilibrium price.
C) government wants to stop a deflationary spiral.
D) government is imposing a legal price that is typically above the equilibrium price.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A decrease in supply of X increases the equilibrium price of X,which reduces the demand for X and automatically returns the price of X to its initial level.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If two goods are complements:
A) they are consumed independently.
B) an increase in the price of one will increase the demand for the other.
C) a decrease in the price of one will increase the demand for the other.
D) they are necessarily inferior goods.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Graphically,the market demand curve is:
A) steeper than any individual demand curve that is part of it.
B) greater than the sum of the individual demand curves.
C) the horizontal sum of individual demand curves.
D) the vertical sum of individual demand curves.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
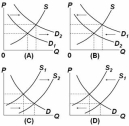 Which of the above diagrams illustrate(s) the effect of an increase in automobile worker wages on the market for automobiles?
Which of the above diagrams illustrate(s) the effect of an increase in automobile worker wages on the market for automobiles?
A) A only.
B) B only.
C) C only.
D) D only.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Perfectly competitive markets explained on the basis of supply and demand:
A) assume many buyers and many sellers of a standardized product.
B) assume market power so that buyers and sellers bargain with one another.
C) do not exist in the real-world economy.
D) are approximated by markets in which a single seller determines price.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If Z is an inferior good,an increase in money income will shift the:
A) supply curve for Z to the left.
B) supply curve for Z to the right.
C) demand curve for Z to the left.
D) demand curve for Z to the right.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The relationship between quantity supplied and price is _____ and the relationship between quantity demanded and price is _____.
A) direct,inverse
B) inverse,direct
C) inverse,inverse
D) direct,direct
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An improvement in production technology will:
A) increase equilibrium price.
B) shift the supply curve to the left.
C) shift the supply curve to the right.
D) shift the demand curve to the left.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true about price ceilings?
A) Price ceilings cause goods to be rationed by prices.
B) Price ceilings cause goods to be rationed by some other means than free market prices.
C) Ration coupons are the only way to ration goods when price ceilings are in place.
D) All of the above statements are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Supply refers to the amount of a product that a producer will offer in the market at some particular price.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the price of a product will reduce the amount of it purchased because:
A) supply curves are upsloping.
B) the higher price means that real incomes have risen.
C) consumers will substitute other products for the one whose price has risen.
D) consumers substitute relatively high-priced for relatively low-priced products.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The location of the supply curve of a product depends on:
A) the technology used to produce it.
B) the prices of resources used in its production.
C) the number of sellers in the market.
D) all of these.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
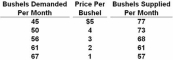 Refer to the above data.Equilibrium price is:
Refer to the above data.Equilibrium price is:
A) $4.
B) $3.
C) $2.
D) $1.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
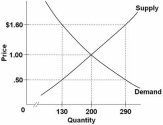 Refer to the above diagram.The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be:
Refer to the above diagram.The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be:
A) $1.00 and 200.
B) $1.60 and 130.
C) $.50 and 130.
D) $1.60 and 290.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If X is a normal good,a rise in money income will shift the:
A) supply curve for X to the left.
B) supply curve for X to the right.
C) demand curve for X to the left.
D) demand curve for X to the right.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 179
Related Exams