If there are external benefits or positive externalities associated with the consumption of a good or service:
A) the private demand curve will overestimate the true demand curve.
B) the private demand curve will underestimate the true demand curve.
C) consumers will be willing to pay for all these benefits in private markets.
D) the market demand curve will be the vertical summation of the individual demand costs.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
The following information is for a public good.Pa and Pb are the prices that individuals A and B are willing to pay for the last unit of a public good,rather than do without it.These people are the only two members of society.
Refer to the data below.If the marginal cost of this good at the optimal quantity is $4,the optimal quantity must be: 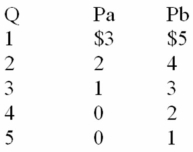
A) 1 unit.
B) 2 units.
C) 3 units.
D) 4 units.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified