A) Inequity.
B) Internalities.
C) Public goods.
D) Production possibilities.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to cost-benefit analysis, a government project should be undertaken as long as the
A) Opportunity costs exceed the welfare benefits.
B) Benefits exceed the opportunity costs.
C) Benefits equal the costs.
D) Voters approve the project.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Approximately what percentage of state and local expenditures do bond referenda account for?
A) Less than 1 percent.
B) 10 percent.
C) 25 percent.
D) 50 percent.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When external costs result from the production of a good,
A) Producers have an incentive to produce too little.
B) Consumers have an incentive to consume too little.
C) Both producers and consumers have an incentive to produce and consume too much.
D) Producers and consumers are not affected.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the best example of a government effort to address market failure in relation to the FOR WHOM to produce question?
A) Antitrust policy.
B) Regulations reducing pollution.
C) Transfer payments.
D) The production of goods that allow free riders.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following properly ranks the size of tax revenues received by the federal government from highest to lowest?
A) Excise taxes, Social Security payroll taxes, income taxes, and corporate taxes.
B) Corporate taxes, Social Security payroll taxes, income taxes, and excise taxes.
C) Income taxes, Social Security payroll taxes, corporate taxes, and excise taxes.
D) Social Security payroll taxes, excise taxes, corporate taxes, and income taxes.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a source of government failure but is not typically an example of market failure?
A) Monopoly.
B) Externalities.
C) Inequity.
D) Waste.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
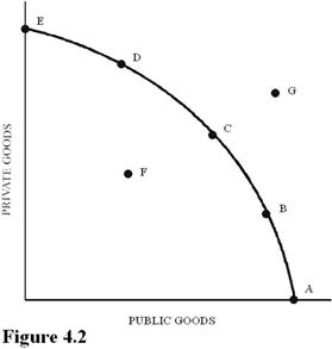 Using Figure 4.2, suppose point C represents the optimal mix of public and private goods for a society.The market mechanism is likely to result in a mix of output represented by point
Using Figure 4.2, suppose point C represents the optimal mix of public and private goods for a society.The market mechanism is likely to result in a mix of output represented by point
A) F because the market mechanism is inefficient.
B) B because the market mechanism tends to overproduce public goods.
C) C because the market mechanism is efficient.
D) D because the market mechanism tends to underproduce public goods.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the cost-benefit analysis of public goods, the benefits
A) Can be accurately measured using the market price of the public good.
B) Can be accurately measured by ballot box economics.
C) Are more easily estimated than the costs.
D) Can be only roughly estimated using highly subjective techniques.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Public choice theory emphasizes the role of self-interest in public decision making.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a sound economic reason why the government should subsidize your college education?
A) To help the school's monopoly power over private schools.
B) It is too expensive.
C) There are external benefits associated with education.
D) The profit motive would cause the private sector to overproduce education.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Market failure implies that the market mechanism
A) Leads the economy to a point outside the production possibilities curve.
B) Leads the economy to the wrong mix of output.
C) Causes shortages or surpluses in the market.
D) Causes government failure.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Government intervention can serve to stabilize the macro economy by
A) Reducing inflation and encouraging the equitable distribution of income.
B) Reducing employment and encouraging economic growth.
C) Regulating monopolies and encouraging the equitable distribution of output.
D) Reducing inflation and encouraging economic growth.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
As long as a public sector activity will generate benefits regardless of the costs, the activity should definitely be undertaken.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The optimal mix of output is the most desirable combination of output attainable with existing
A) Resources and products.
B) Resources, technology, and social values.
C) Resources, government regulations, and technology.
D) Technology and business decisions.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A tax that is placed on the quantity of the item purchased, such as gallons of it, is called a(n)
A) Income tax.
B) Property tax.
C) Excise tax.
D) None of the choices are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following explains what would happen if public goods were marketed like private goods?
A) Public goods would be underproduced.
B) Many consumers would want to buy the goods.
C) Public goods would be overproduced.
D) Government failure would result.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that if your income is $100,000, your tax is $20,000, but if your income is $200,000, your tax is $45,000.Such a tax is
A) Regressive.
B) Progressive.
C) Proportional.
D) A flat tax.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a progressive tax?
A) Social Security payroll tax.
B) A local sales tax.
C) The federal income tax.
D) An excise tax.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Markets will underproduce goods that yield external benefits and overproduce those that generate external costs.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 151
Related Exams