A) quarks
B) leptons
C) fermions
D) bosons
E) None of these is correct.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The time-independent Schrödinger equation is
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The quantum phenomenon known as the "tunnel effect" refers to
A) highly eccentric electron orbits penetrating inner closed shells.
B) the fine structure exhibited by many spectral lines.
C) the small but finite probability that an -particle originally within the nucleus will be found outside the nucleus.
D) the penetration of shielding by high-energy fission neutrons.
E) an orbital electron penetrating the nucleus and undergoing electron capture.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) A particle that is confined to some region of space can have zero energy.
B) All phenomena in nature are adequately described by classical wave theory.
C) The Schrödinger equation can be derived from Newton's laws of motion.
D) The penetration of a barrier by a wave has physical significance.
E) None of these is true.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You put 5 non-interacting identical fermions each of mass m into a 1-d box of dimension L.You then put 10 non-interacting bosons each of mass m into a 1-d box of length 2L.Which system has the lowest ground-state energy and what is the value of the fermion system ground-state energy divided by the boson system ground-state energy?
A) fermion system,19/10
B) boson system,10/19
C) boson system,38/5
D) fermion system,5/19
E) none of the above
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The energy in the first excited state of an electron confined to a one-dimensional box of length L = 0.3 nm is
A) 9.40 eV
B) 12.3 eV
C) 16.7 eV
D) 24.2 eV
E) 37.6 eV
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particle of kinetic energy E0 traveling in a region in which the potential energy is zero is then incident on a potential barrier of height U0.What is the ratio of E0/U0 so that the reflection co-efficient is 75%? (Assume E0 is much less than the rest mass energy of the particle.)
A) 1.250
B) 0.7500
C) 1.778
D) 1.005
E) 1.063
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The wave function for a particle in a one-dimensional box of length L
A) is constrained by the boundary conditions 0) = 0 and (L) = 0.
B) must be zero everywhere outside of the box.
C) is given by (x) = A sin kx,where A is a constant.
D) restricts the possible energy of the particle to E = ![]() .
.
E) All of these are correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A proton of energy E0 traveling in a region in which the potential energy is zero is incident on a potential barrier of height U0 = 0.5E0.The probability that the proton will be transmitted is
A) 85.3%
B) 89.2%
C) 92.4%
D) 97.1%
E) 98.3%
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron confined to a one-dimensional box of length L = 0.2 nm makes a transition from state n = 4 to state n = 3.The wavelength of the photon emitted is
A) 19.0 nm
B) 17.2 nm
C) 14.6 nm
D) 12.5 nm
E) 10.8 nm
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Schrödinger equation
A) is a partial differential equation in space and time.
B) (like Newton's laws of motion) cannot be derived.
C) depends upon experimentation for its verification.
D) relates the second space-derivative of the wave function to the first time-derivative of the wave function.
E) All of these are correct.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron of kinetic energy E0 traveling in a region in which the potential energy is zero is then incident on a finite potential barrier of height U0 (= 4E0) and width a.If the potential barrier is reduced to 2E0,by what factor will the probability of penetration of the barrier be changed?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) None of these is correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match each of the wave function on the left for a particle in a finite square well with the corresponding probability distributions on the right,in the order (a) ,(b) ,and (c) . 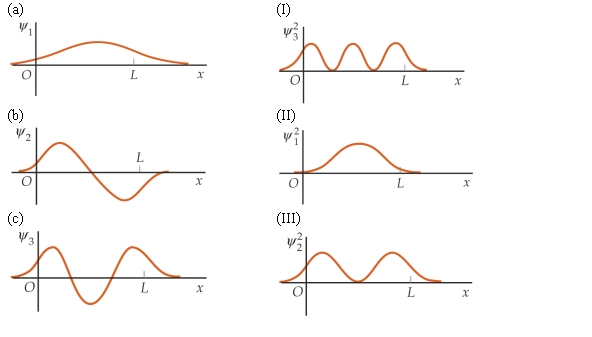
A) (II) (I) (III)
B) (II) (III) (I)
C) (III) (I) (II)
D) (III) (II) (I)
E) (I) (III) (II)
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The solution for the time-independent Schrödinger equation with the following potential function and boundary conditions  is
is
A) ![]() ,where
,where ![]() and n = 1,2,3,..
and n = 1,2,3,..
B) ![]() ,where
,where ![]() and n = 1,2,3,..
and n = 1,2,3,..
C) ![]() ,where
,where ![]() and n = 1,2,3,..
and n = 1,2,3,..
D) ![]() ,where
,where ![]() and n = 1,2,3,..
and n = 1,2,3,..
E) There is no solution for the given potential function and boundary conditions.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The energy in the ground state of an electron confined to a one-dimensional box of length L = 0.2 nm is
A) 1.88 eV
B) 4.47 eV
C) 6.25 eV
D) 9.40 eV
E) None of these is correct.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particle of energy E0 traveling in a region in which the potential energy is zero is incident on a potential barrier of height U0 = 0.4E0.The probability that the particle will be reflected is
A) 0.316%
B) 0.789%
C) 1.61%
D) 3.56%
E) 4.12%
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The energy in the first excited state of an electron confined to a one-dimensional box of length L = 0.2 nm is
A) 9.40 eV
B) 12.3 eV
C) 19.7 eV
D) 24.2 eV
E) 37.6 eV
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the natural frequency of oscillation for H2 is 1012 Hz,the effective spring constant between the two H atoms is of the order
A) 10-1 N/m
B) 10-3 N/m
C) 10-5 N/m
D) 10-7 N/m
E) 10-9 N/m
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particle of energy E0 traveling in a region in which the potential energy is zero is incident on a potential barrier of height U0 = 0.3E0.The probability that the particle will be reflected is
A) 0.316%
B) 0.791%
C) 2.89%
D) 3.56%
E) 4.12%
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In three dimensions,the Schrödinger equation for the infinite square-well potential
A) has a solution of the form (x,y,z) = A sin k1x sin k2y sin k3z,where the k's are wave numbers and the constant A is determined by normalization.
B) predicts energy states described by ![]() .
.
C) predicts energies and wave functions that are characterized by three quantum numbers.
D) allows multiple quantum states corresponding to the same energy level.
E) All of these are true.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 42
Related Exams