A) u2 = v2 - 2g(a - b)
B) u2 = v2 + 2g(a + b)
C) u2 = v2 + 2g(a - b)
D) u2 = v2 + 2g(b - a)
E) u2 = v2 + g(a - b)
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the work done by a force, 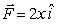 , along the path (0,0) P1 (2,0) P2 (2,2) .
, along the path (0,0) P1 (2,0) P2 (2,2) . 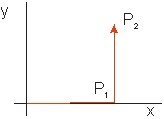
A) 2 J
B) 4 J
C) 6 J
D) 8 J
E) 10 J
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are units of energy?
A) MeV
B) MeV·c2
C) c2/MeV
D) 1/MeV
E) MeV/c2
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A) The work done by a conservative force on an object is independent on the path taken.
B) The work done by a conservative force on an object along path A B is negative that of path B A.
C) The force due to gravity is an example of a conservative force.
D) Friction is an example of a conservative force.
E) The work done by friction on an object depends on the path taken.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
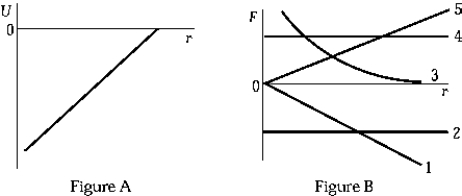 When the potential energy U(r) is given as in Figure A, then the force is given in Figure B by curve
When the potential energy U(r) is given as in Figure A, then the force is given in Figure B by curve
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A block of mass, m, is pushed up against a spring, compressing it a distance x, and is then released. The spring projects the block along a frictionless horizontal surface, giving the block a speed v. The same spring projects a second block of mass 4m, giving it a speed 3v. What distance was the spring compressed in the second case?
A) x
B) 2x
C) 3x
D) 4x
E) 6x
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
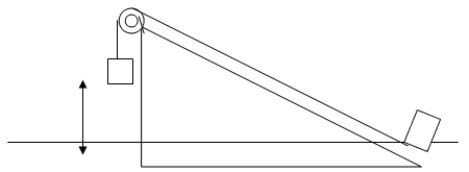 A hanging block A (mA = 15 kg) is connected by a light cable and a pulley wheel to a second block B (mB = 10 kg) situated at the bottom of a frictionless inclined plane with angle 30 to the horizontal. If the hanging block is released from rest 5 m above the ground, find the maximum distance that block B travels up along the inclined plane.
A hanging block A (mA = 15 kg) is connected by a light cable and a pulley wheel to a second block B (mB = 10 kg) situated at the bottom of a frictionless inclined plane with angle 30 to the horizontal. If the hanging block is released from rest 5 m above the ground, find the maximum distance that block B travels up along the inclined plane.
A) 9.0 m
B) 4.0 m
C) 2.3 m
D) 7.3 m
E) 6.5 m
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assuming the incline to be frictionless and the zero of gravitational potential energy to be at the elevation of the horizontal line, 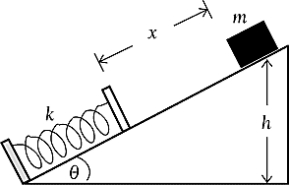
A) the kinetic energy of the block just before it collides with the spring will be equal to mgh.
B) the kinetic energy of the block when it has fully compressed the spring will be equal to mgh.
C) the potential energy of the block when it has fully compressed the spring will be zero.
D) the energy stored in the spring plus the gravitational potential energy of the block when it has fully compressed the spring will be equal to mgh.
E) None of the above statements will be true.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Friction is a conservative force and does negative work.
B) Potential energy may be defined by the equation U(x) = -dF(x) /dx
C) The work done by a conservative force between two points depends on the path taken between those points.
D) A conservative force cannot change a body's total energy.
E) The work done by a conservative force while a body moves at constant velocity must be zero.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reference point for gravitational potential energy
A) must be at the initial position of the object.
B) must be at the final position of the object.
C) must be at ground level.
D) must be at the lowest position ever reached by the object.
E) can be chosen arbitrarily.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure to the right to answer the next problems.
An object of mass m = 100 g slides down without rolling a rough incline from a height H = 60 cm. At
h = 30 cm, the object flies off the incline. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.4, and the angle = 30 . 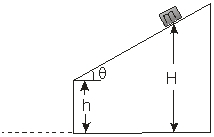 -The minimum amount of energy released in an electron-positron annihilation is
-The minimum amount of energy released in an electron-positron annihilation is
A) 0
B) 0.511 MeV
C) 1.022 MeV
D) 2.044 MeV
E) None of these is correct.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure to the right to answer the next problems.
An object of mass m = 100 g slides down without rolling a rough incline from a height H = 60 cm. At
h = 30 cm, the object flies off the incline. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.4, and the angle = 30 .  -How far from the base of the elevated incline does the object hit the floor?
-How far from the base of the elevated incline does the object hit the floor?
A) 14.8 cm
B) 17.5 cm
C) 21.9 cm
D) 24.6 cm
E) None of these is correct.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
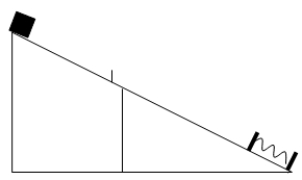 A 3-kg block sits on an incline where the top half of the incline has a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.5 and the bottom half is frictionless. The angle of inclination is 35 degrees. If the block is released and travels 10 m along the rough part of the incline and then 10 m along the smooth part before it makes contact with the spring (k = 200 N/m) , calculate the distance the spring is compressed.
A 3-kg block sits on an incline where the top half of the incline has a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.5 and the bottom half is frictionless. The angle of inclination is 35 degrees. If the block is released and travels 10 m along the rough part of the incline and then 10 m along the smooth part before it makes contact with the spring (k = 200 N/m) , calculate the distance the spring is compressed.
A) 1.47 m
B) 1.56 m
C) 2.16 m
D) 2.43 m
E) 1.39 m
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mass m is released from a height 60 cm from the right-hand side of the track shown in the diagram at right. There is only friction acting on the mass on the horizontal portion 35 cm either side of the midpoint O, with a kinetic coefficient of friction of k = 0.5. Determine what is the velocity of the block the first time it passes through the midpoint, and on which side of the midpoint does it stop? 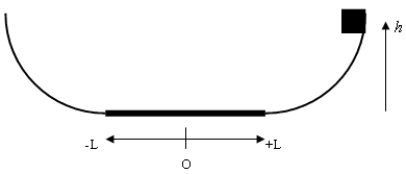
A) 3.4 m/s, R
B) 3.9 m/s, R
C) 3.9 m/s, L
D) 2.9 m/s, L
E) 2.9 m/s, R
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
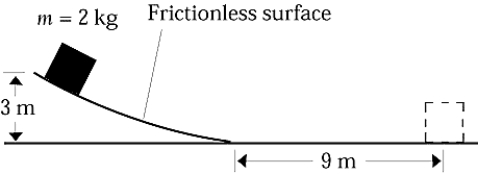 The block shown in the figure is sliding on a frictionless surface. Its speed when it has traveled 9 m along the horizontal surface will be
The block shown in the figure is sliding on a frictionless surface. Its speed when it has traveled 9 m along the horizontal surface will be
A) 3.14 m/s
B) 7.67 m/s
C) 9.81 m/s
D) 13.3 m/s
E) None of these is correct.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a hydrogen atom absorbs a photon with E = 4.089 10-19 J, what is the frequency of the photon?
A) 6.17 1014 Hz
B) 2.45 1018 Hz
C) 2.55 108 Hz
D) 6.623 1034 Hz
E) None of these is correct.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
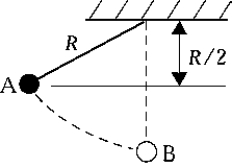 Release mass m on a string from rest at point A. As it passes the lowest point B, the tension in the string is
Release mass m on a string from rest at point A. As it passes the lowest point B, the tension in the string is
A) impossible to determine; the answer depends on the length of the string.
B) mg
C) 2mg
D) 3mg
E) None of these is correct.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A child is sitting on the seat of a swing with ropes 10 m long. Her father pulls the swing back until the ropes make a 37º angle with the vertical and then releases the swing. If air resistance is neglected, what is the speed of the child at the bottom of the arc of the swing when the ropes are vertical?
A) 11 m/s
B) 8.8 m/s
C) 14 m/s
D) 6.3 m/s
E) 12 m/s
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rest mass of an electron is 9.11 10-31 kg. From this information one can conclude that the rest energy of an electron is
A) 8.20 10-14 MeV
B) 0.512 MeV
C) 2.73 10-22 J
D) 0.00171 MeV
E) 0.171 MeV
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you drive at the posted speed limit of 70 mph on the interstate, what is the fraction of your speed compared to the speed of light?
A) 6.48 10-8
B) 1.04 10-7
C) 2.33 10-7
D) 3.73 10-7
E) None of these is correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 73
Related Exams