A) a base-pair deletion
B) a codon substitution
C) a substitution in the last base of a codon
D) a codon deletion
E) a point mutation
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following model of a eukaryotic transcript to answer the next few questions. 5' UTR E1 I1 E2 I2 E3 I3 E4 UTR 3' -When the spliceosome binds to elements of this structure, where can it attach?
A) to the exons
B) to the 5' UTR
C) to the 3' UTR
D) to an adjacent intron and exon
E) to the end of an intron
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During splicing, which molecular component of the spliceosome catalyzes the excision reaction?
A) protein
B) DNA
C) RNA
D) lipid
E) sugar
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to the simple metabolic pathway in Figure 14.1.
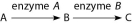 Figure 14.1
-According to Beadle and Tatum's hypothesis, how many genes are necessary for this pathway?
Figure 14.1
-According to Beadle and Tatum's hypothesis, how many genes are necessary for this pathway?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) It cannot be determined from the pathway.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes the significance of the TATA box in eukaryotic promoters?
A) It is the recognition site for a specific transcription factor.
B) It sets the reading frame of the mRNA.
C) It prevents supercoiling of the DNA near the start site.
D) It is the recognition site for ribosomal binding.
E) Its significance has not yet been determined.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A part of the promoter, called the TATA box, is said to be highly conserved in evolution. Which of the following might this illustrate?
A) The sequence evolves very rapidly.
B) The sequence does not mutate.
C) Any mutation in the sequence is selected against.
D) The sequence is found in many but not all promoters.
E) The sequence is transcribed at the start of every gene.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In eukaryotic cells, transcription cannot begin until
A) the two DNA strands have completely separated and exposed the promoter.
B) several transcription factors have bound to the promoter.
C) the 5' caps are removed from the mRNA.
D) the DNA introns are removed from the template.
E) DNA nucleases have isolated the transcription unit.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following nucleotide triplets best represents a codon?
A) a triplet separated spatially from other triplets
B) a triplet that has no corresponding amino acid
C) a triplet at the opposite end of tRNA from the attachment site of the amino acid
D) a triplet in the same reading frame as an upstream AUG
E) a sequence in tRNA at the 3' end
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order for a eukaryotic gene to be engineered into a bacterial colony to be expressed, what must be included in addition to the coding exons of the gene?
A) the introns
B) eukaryotic polymerases
C) a bacterial promoter sequence
D) eukaryotic ribosomal subunits
E) eukaryotic tRNAs
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following experimental procedures is most likely to hasten mRNA degradation in a eukaryotic cell?
A) enzymatic lengthening of the poly-A tail
B) removal of the 5' cap
C) methylation of C nucleotides
D) methylation of histones
E) removal of one or more exons
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes the termination of transcription in prokaryotes?
A) RNA polymerase transcribes through the polyadenylation signal, causing proteins to associate with the transcript and cut it free from the polymerase.
B) RNA polymerase transcribes through the terminator sequence, causing the polymerase to separate from the DNA and release the transcript.
C) RNA polymerase transcribes through an intron, and the snRNPs cause the polymerase to let go of the transcript.
D) Once transcription has initiated, RNA polymerase transcribes until it reaches the end of the chromosome.
E) RNA polymerase transcribes through a stop codon, causing the polymerase to stop advancing through the gene and release the mRNA.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the 1920s, Muller discovered that X-rays caused mutation in Drosophila. In a related series of experiments in the 1940s, Charlotte Auerbach discovered that chemicals-she used nitrogen mustards-have a similar effect. A new chemical food additive is developed by a cereal manufacturer. Why do we test for its ability to induce mutation?
A) We worry that it might cause mutation in cereal grain plants.
B) We want to make sure that it does not emit radiation.
C) We want to be sure that it increases the rate of mutation sufficiently.
D) We want to prevent any increase in mutation frequency.
E) We worry about its ability to cause infection.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The process of translation, whether in prokaryotes or eukaryotes, requires tRNAs, amino acids, ribosomal subunits, and which of the following?
A) polypeptide factors plus ATP
B) polypeptide factors plus GTP
C) polymerases plus GTP
D) SRP plus chaperones
E) signal peptides plus release factor
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following mutations is most likely to cause a phenotypic change?
A) a duplication of all or most introns
B) a large inversion whose ends are each in the same region between genes
C) a nucleotide substitution in an exon coding for a transmembrane domain
D) a single nucleotide deletion in an exon coding for an active site
E) a frameshift mutation one codon away from the 3' end of the nontemplate strand
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to the simple metabolic pathway in Figure 14.1.
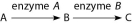 Figure 14.1
-If A, B, and C are all required for growth, a strain that is mutant for the gene-encoding enzyme A would be able to grow on which of the following media?
Figure 14.1
-If A, B, and C are all required for growth, a strain that is mutant for the gene-encoding enzyme A would be able to grow on which of the following media?
A) minimal medium
B) minimal medium supplemented with nutrient A only
C) minimal medium supplemented with nutrient B only
D) minimal medium supplemented with nutrient C only
E) minimal medium supplemented with nutrients A and C
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true about protein synthesis in prokaryotes?
A) Extensive RNA processing is required before prokaryotic transcripts can be translated.
B) Translation can begin while transcription is still in progress.
C) Prokaryotic cells have complicated mechanisms for targeting proteins to the appropriate cellular organelles.
D) Translation requires antibiotic activity.
E) Unlike eukaryotes, prokaryotes require no initiation or elongation factors.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nitrogenous base adenine is found in all members of which group?
A) proteins, triglycerides, and testosterone
B) proteins, ATP, and DNA
C) ATP, RNA, and DNA
D) α glucose, ATP, and DNA
E) proteins, carbohydrates, and ATP
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which small-scale mutation would be most likely to have a catastrophic effect on the functioning of a protein?
A) a base substitution
B) a base deletion near the start of a gene
C) a base deletion near the end of the coding sequence, but not in the terminator codon
D) deletion of three bases near the start of the coding sequence, but not in the initiator codon
E) a base insertion near the end of the coding sequence, but not in the terminator codon
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When translating secretory or membrane proteins, ribosomes are directed to the ER membrane by
A) a specific characteristic of the ribosome itself, which distinguishes free ribosomes from bound ribosomes.
B) a signal-recognition particle that brings ribosomes to a receptor protein in the ER membrane.
C) moving through a specialized channel of the nucleus.
D) a chemical signal given off by the ER.
E) a signal sequence of RNA that precedes the start codon of the message.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Alternative RNA splicing
A) is a mechanism for increasing the rate of transcription.
B) can allow the production of proteins of different sizes and functions from a single mRNA.
C) can allow the production of similar proteins from different RNAs.
D) increases the rate of transcription.
E) is due to the presence or absence of particular snRNPs.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 83
Related Exams