A) at the NH3 end.
B) at the COO- end.
C) along the exterior face of the membrane.
D) at the loop between helices 5 and 6.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
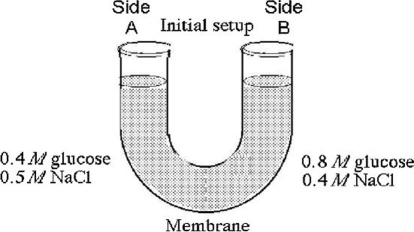 Figure 5.3
The solutions in the arms of a U-tube (Figure 5.3) are separated at the bottom of the tube by a selectively permeable membrane. The membrane is permeable to sodium chloride but not to glucose. Side A is filled with a solution of 0.4 M glucose and 0.5 M sodium chloride (NaCl) , and side B is filled with a solution containing 0.8 M glucose and 0.4 M sodium chloride. Initially, the volume in both arms is the same. Refer to the figure to answer the following questions.
-If you examine side A in the figure after three days, the concentrations of glucose and NaCl should be
Figure 5.3
The solutions in the arms of a U-tube (Figure 5.3) are separated at the bottom of the tube by a selectively permeable membrane. The membrane is permeable to sodium chloride but not to glucose. Side A is filled with a solution of 0.4 M glucose and 0.5 M sodium chloride (NaCl) , and side B is filled with a solution containing 0.8 M glucose and 0.4 M sodium chloride. Initially, the volume in both arms is the same. Refer to the figure to answer the following questions.
-If you examine side A in the figure after three days, the concentrations of glucose and NaCl should be
A) 0.4 M glucose, 0.45 M NaCl.
B) 0.6 M glucose, 0.5 M NaCl.
C) 0.6 M glucose, 0.45 M NaCl.
D) 0.8 M glucose, 0.4 M NaCl.
E) 0.8 M glucose, 0.5 M NaCl.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Familial hypercholesterolemia is characterized by extremely high levels of cholesterol in the blood, which results from
A) defective cell membranes that cannot incorporate cholesterol.
B) poor attachment of cholesterol to the extracellular matrix of cells.
C) inhibition of the cholesterol active transport system in red blood cells.
D) nonfunctional or missing LDL receptors on cell membranes.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary function of kinases in signal transduction is to
A) inactivate relay molecule to turn off signal transduction.
B) regulate gene expression by serving as a transcription factor.
C) inactivate second messengers such as cAMP.
D) activate protein kinases or other relay molecules in a series.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Phosphorylation cascades involving a series of protein kinases are useful for cellular signal transduction because
A) they are species specific.
B) they always lead to the same cellular response.
C) they amplify the original signal manyfold.
D) they counter the harmful effects of phosphatases.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are lipids and proteins free to move laterally in membranes?
A) The interior of the membrane is filled with liquid water.
B) Lipids and proteins repulse each other in the membrane.
C) Phospholipids form hydrogen bonds with water at the membrane surface, which moves the lipids as water moves.
D) Weak hydrophobic interactions in the interior of the membrane are easily disrupted.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following ways could signal transduction most probably be explored in research to treat cancer?
A) removal of serine/threonine phosphate acceptors from transduction pathways in colon pre-cancerous growths
B) increase in calcium ion uptake into the cytoplasm in order to modulate the effects of environmental carcinogens
C) alteration of protein kinases in cell cycle regulation in order to slow cancer growth
D) stimulation of cAMP production in cancer cells
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Glucose diffuses slowly through artificial phospholipid bilayers. The cells lining the small intestine, however, rapidly move large quantities of glucose from the glucose-rich food into their glucose-poor cytoplasm. Based on this information, which transport mechanism is most likely responsible for glucose transport in the intestinal cells?
A) simple diffusion
B) phagocytosis
C) active transport pumps
D) facilitated diffusion
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lipid-soluble signaling molecules, such as aldosterone, cross the membranes of all cells but affect only target cells because
A) only target cells retain the appropriate DNA segments.
B) intracellular receptors are present only in target cells.
C) only target cells have enzymes that break down aldosterone.
D) only in target cells is aldosterone able to initiate a phosphorylation cascade that turns genes on.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis is that
A) pinocytosis brings only water molecules into the cell, whereas receptor-mediated endocytosis brings in other molecules as well.
B) pinocytosis increases the surface area of the plasma membrane, whereas receptor-mediated endocytosis decreases the plasma membrane surface area.
C) pinocytosis is nonselective in the molecules it brings into the cell, whereas receptor-mediated endocytosis is highly selective.
D) pinocytosis requires cellular energy, but receptor-mediated endocytosis does not.
E) pinocytosis can concentrate substances from the extracellular fluid, but receptor-mediated endocytosis cannot.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The movement of the hydrophobic gas nitrous oxide (N2O) (laughing gas) into a cell is an example of
A) active transport across the lipid bilayer.
B) facilitated diffusion through the lipid bilayer.
C) diffusion through the lipid bilayer.
D) osmosis through the lipid bilayer.
E) cotransport across the lipid bilayer.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of integral membrane proteins?
A) They serve only a structural role in membranes.
B) They are loosely bound to the surface of the bilayer.
C) They are usually transmembrane proteins.
D) They are not mobile within the bilayer.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
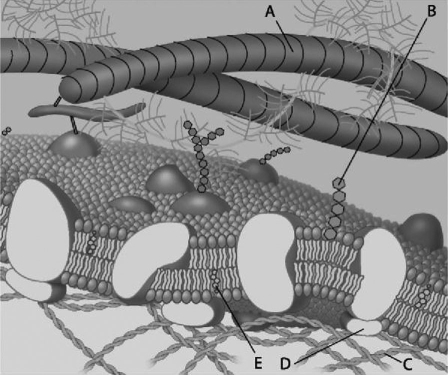 Figure 5.1
For the following questions, match the labeled component of the cell membrane in Figure 5.1 with its description.
-Which component in the figure helps membranes resist changes in fluidity at high and low temperatures?
Figure 5.1
For the following questions, match the labeled component of the cell membrane in Figure 5.1 with its description.
-Which component in the figure helps membranes resist changes in fluidity at high and low temperatures?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 5.1
For the following questions, match the labeled component of the cell membrane in Figure 5.1 with its description.
-Which component in the figure is a glycolipid?
Figure 5.1
For the following questions, match the labeled component of the cell membrane in Figure 5.1 with its description.
-Which component in the figure is a glycolipid?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true for the evolution of cell membranes?
A) The fluid mosaic nature of cell membranes provides for the rapid evolution of cell membranes.
B) The evolution of cell membranes is driven primarily by the evolution of phospholipids as a result of natural selection.
C) The evolution of cell membranes is driven primarily by the evolution of glycoproteins and glycolipids as a result of natural selection.
D) The evolution of cell membranes is driven by the evolution of all membrane components as a result of natural selection.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the fluid mosaic model of cell membranes, which of the following is a true statement about membrane phospholipids?
A) They can move laterally along the plane of the membrane.
B) They frequently flip-flop from one side of the membrane to the other.
C) They occur in an uninterrupted bilayer, with membrane proteins restricted to the surface of the membrane.
D) They are free to depart from the membrane and dissolve in the surrounding solution.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about diffusion is correct?
A) It is very rapid over long distances.
B) It requires an expenditure of energy by the cell.
C) It is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
D) It is an active process in which molecules move from a region of lower concentration to one of higher concentration.
E) It is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
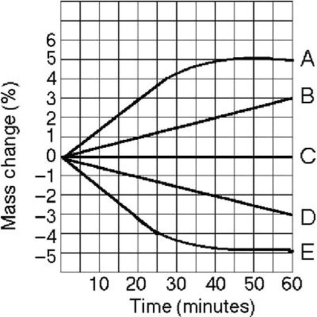 Figure 5.4
Five dialysis bags, constructed from a semipermeable membrane that is impermeable to sucrose, were filled with various concentrations of sucrose and then placed in separate beakers containing an initial concentration of 0.6 M sucrose solution. At 10-minute intervals, the bags were massed (weighed) and the percent change in mass of each bag was graphed. Refer to Figure 5.4 to answer the following question(s) .
-Which line in the graph represents the bag that contained a solution isotonic to the 0.6 M solution at the beginning of the experiment?
Figure 5.4
Five dialysis bags, constructed from a semipermeable membrane that is impermeable to sucrose, were filled with various concentrations of sucrose and then placed in separate beakers containing an initial concentration of 0.6 M sucrose solution. At 10-minute intervals, the bags were massed (weighed) and the percent change in mass of each bag was graphed. Refer to Figure 5.4 to answer the following question(s) .
-Which line in the graph represents the bag that contained a solution isotonic to the 0.6 M solution at the beginning of the experiment?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the first event that occurs following the binding of a ligand by a membrane receptor protein?
A) An intracellular enzyme is activated by phosphorylation.
B) An intracellular G protein is activated.
C) The membrane receptor protein undergoes a conformational change.
D) The membrane receptor protein enters the cytoplasm.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How do unsaturated fatty acids help keep any membrane more fluid at lower temperatures?
A) The double bonds form kinks in the fatty acid tails that prevent adjacent lipids from packing tightly together.
B) Unsaturated fatty acids have a higher cholesterol content that prevents adjacent lipids from packing tightly together.
C) Unsaturated fatty acids are more polar than saturated fatty acids.
D) The double bonds result in shorter fatty acid tails and therefore thinner membranes.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 97
Related Exams