A) preying on animals.
B) ingesting it.
C) consuming living, rather than dead, prey.
D) using enzymes to digest their food.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cycliophorans have two types of larvae. One type of larva is produced when the digestive system of a female is impregnated by a male. The digestive system then collapses and develops into a larva, which swims away in search of a new host after the surrounding female dies. Which is the embryonic tissue that is apparently most important in forming this type of larva?
A) mesoderm
B) ectoderm
C) endoderm
D) mantle
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below. The most recently discovered phylum in the animal kingdom (1995) is the phylum Cycliophora. It includes three species of tiny organisms that live in large numbers on the outsides of the mouthparts and appendages of lobsters. When in the feeding stage, a cycliophoran permanently attaches to the lobster via an adhesive disk and collects scraps of food from its host's feeding by capturing the scraps in a current created by a ring of cilia. Its body is sac-like and has a U-shaped intestine that brings the anus close to the mouth. Cycliophorans are eucoelomate (have a body cavity that is a coelom) and do not molt (though their host does) . -Which of these features is least useful in assigning the phylum Cycliophora to a clade of animals?
A) having a true coelom as a body cavity
B) having a body symmetry that permits a U-shaped intestine
C) lacking ecdysis (molting)
D) its feeding mechanism
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Evidence indicates that an ancestral finch species from South America arrived on the Galapágos Islands and formed many new species, adapting to the diverse environments on the islands. With the evolution of these new bird species on the Galapágos Islands, we would expect to find a corresponding
A) increase in the number of bird parasites on the Galapágos Islands.
B) decrease in the number of bird parasites on the Galapágos Islands.
C) increase in the number of bird parasites in South America.
D) decrease in the number of bird parasites in South America.
E) elimination of bird parasites on the Galapágos Islands.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
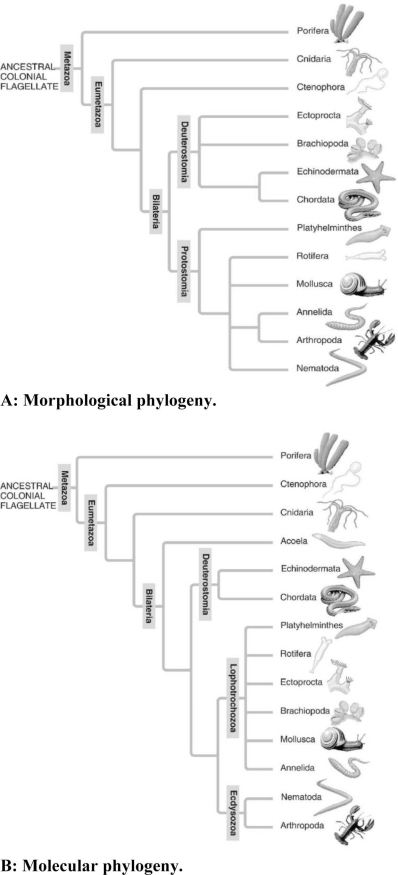 -In the traditional phylogeny (A) , the phylum Platyhelminthes is depicted as a sister taxon to the rest of the protostome phyla and as having diverged earlier from the lineage that led to the rest of the protostomes. In the molecular phylogeny (B) , Platyhelminthes is depicted as a lophotrochozoan phylum. What probably led to this change?
-In the traditional phylogeny (A) , the phylum Platyhelminthes is depicted as a sister taxon to the rest of the protostome phyla and as having diverged earlier from the lineage that led to the rest of the protostomes. In the molecular phylogeny (B) , Platyhelminthes is depicted as a lophotrochozoan phylum. What probably led to this change?
A) Platyhelminthes ceased to be recognized as true protostomes.
B) The removal of the acoel flatworms (Acoela) from the Platyhelminthes allowed the remaining flatworms to be clearly tied to the Lophotrochozoa.
C) All Platyhelminthes must have a well-developed lophophore as their feeding apparatus.
D) Platyhelminthes' close genetic ties to the arthropods became clear as their Hox gene sequences were studied.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below. 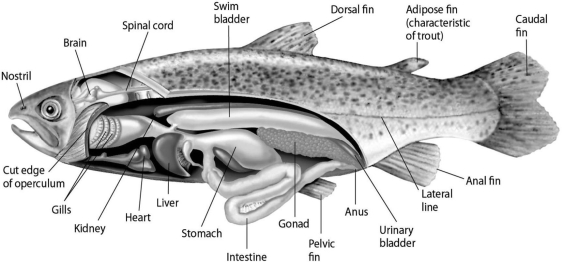 Figure 27.2
Fishes that have swim bladders can regulate their density and thus their buoyancy. There are two types of swim bladder: physostomous and physoclistous. The ancestral version is the physostomous version, in which the swim bladder is connected to the esophagus via a short tube (Figure 27.2) . The fish fills this version by swimming to the surface, taking gulps of air, and directing them into the swim bladder. Air is removed from this version by "belching." The physoclistous version is more derived and has lost its connection to the esophagus. Instead, gas enters and leaves the swim bladder via special circulatory mechanisms within the wall of the swim bladder.
-How do a physoclistous fish and a physotomous fish compare in terms of the amount of energy each must use to maintain its position (depth) in the water column over the long term?
Figure 27.2
Fishes that have swim bladders can regulate their density and thus their buoyancy. There are two types of swim bladder: physostomous and physoclistous. The ancestral version is the physostomous version, in which the swim bladder is connected to the esophagus via a short tube (Figure 27.2) . The fish fills this version by swimming to the surface, taking gulps of air, and directing them into the swim bladder. Air is removed from this version by "belching." The physoclistous version is more derived and has lost its connection to the esophagus. Instead, gas enters and leaves the swim bladder via special circulatory mechanisms within the wall of the swim bladder.
-How do a physoclistous fish and a physotomous fish compare in terms of the amount of energy each must use to maintain its position (depth) in the water column over the long term?
A) a physoclistous fish uses more energy than a physostomous fish
B) a physostomous fish uses more energy than a physoclistous fish
C) a physoclistous fish and a physostomous fish use the same amount of energy
D) a physoclistous fish initially uses more energy than a physostomous fish but then decreases its energy use to be equal to the physostomous fish
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below.  Figure 27.2
Fishes that have swim bladders can regulate their density and thus their buoyancy. There are two types of swim bladder: physostomous and physoclistous. The ancestral version is the physostomous version, in which the swim bladder is connected to the esophagus via a short tube (Figure 27.2) . The fish fills this version by swimming to the surface, taking gulps of air, and directing them into the swim bladder. Air is removed from this version by "belching." The physoclistous version is more derived and has lost its connection to the esophagus. Instead, gas enters and leaves the swim bladder via special circulatory mechanisms within the wall of the swim bladder.
-Which graph properly depicts the relationship between the amount of gas in the swim bladder and the density of the fish?
Figure 27.2
Fishes that have swim bladders can regulate their density and thus their buoyancy. There are two types of swim bladder: physostomous and physoclistous. The ancestral version is the physostomous version, in which the swim bladder is connected to the esophagus via a short tube (Figure 27.2) . The fish fills this version by swimming to the surface, taking gulps of air, and directing them into the swim bladder. Air is removed from this version by "belching." The physoclistous version is more derived and has lost its connection to the esophagus. Instead, gas enters and leaves the swim bladder via special circulatory mechanisms within the wall of the swim bladder.
-Which graph properly depicts the relationship between the amount of gas in the swim bladder and the density of the fish? 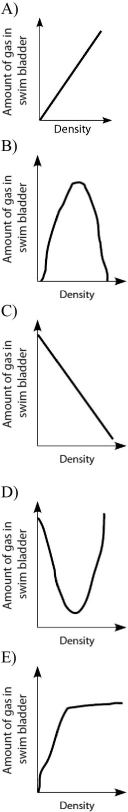
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Organisms at which of the following trophic levels increased the most because of the movement of animals onto land?
A) herbivores and carnivores
B) decomposers and producers
C) producers
D) decomposers
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Among the invertebrate phyla, phylum Arthropoda is unique in possessing members that have
A) a cuticle.
B) a ventral nerve cord.
C) open circulation.
D) wings.
E) segmented bodies.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In terms of food capture, which sponge cell is most similar to the cnidocyte of a cnidarian?
A) amoebocyte
B) choanocyte
C) epidermal cell
D) gastrovascular cavity cell
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below. An elementary school science teacher decided to liven up the classroom with a saltwater aquarium. Knowing that saltwater aquaria can be quite a hassle, the teacher proceeded stepwise. First, the teacher conditioned the water. Next, the teacher decided to stock the tank with various marine invertebrates, including a sea star, a sponge, a sea urchin, a jellyfish, several hermit crabs, some sand dollars, and an ectoproct. Last, she added some vertebrates - a parrotfish and a clownfish. She arranged for daily feedings of copepods and feeder fish. -One day, Tommy (a student in an undersupervised class of 40 fifth graders) got the urge to pet Nemo (the clownfish) , who was swimming among the waving petals of a pretty underwater "flower" that had a big hole in the midst of the petals. Tommy giggled upon finding that these petals felt sticky. A few hours later, Tommy was in the nurse's office with nausea and cramps. Microscopic examination of his fingers would probably have revealed the presence of
A) teeth marks.
B) spines.
C) spicules.
D) nematocysts.
E) a radula.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below.
Placozoan evolutionary relationships to other animals are currently unclear, and different phylogenies can be created, depending on the characters used to infer relatedness. Placozoans are multicellular invertebrates with a simple structure of only two tissue layers and only four cell types. They have the smallest amount of DNA measured in any animal. In comparison, sponges have no tissues but about 20 cell types. One species of placozoans, Tp (Trichoplax adhaerens) , produces a neuropeptide almost identical to one found in cnidarians. The genome of Tp, although the smallest of any known animal, shares many features of complex eumetazoan (even human!) genomes. The next three questions refer to the phylogenetic trees that follow. In the trees, the outgroup is a taxon that is outside the group of interest; members of the group of interest are more closely related to one another than to the outgroup. 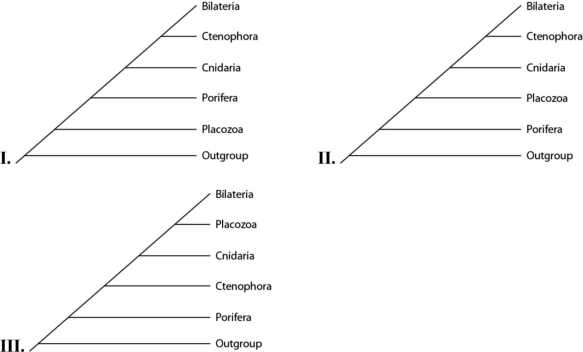 -Which tree(s) has (have) been created by emphasizing the structural simplicity of placozoans?
-Which tree(s) has (have) been created by emphasizing the structural simplicity of placozoans?
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and III
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Internal fertilization, leathery amniotic eggs, and skin that resists drying are characteristics of which extant vertebrate group?
A) amphibians
B) non-bird reptiles
C) chondrichthyans
D) mammals
E) birds.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement is most consistent with the hypothesis that the Cambrian explosion was caused by the rise of predator-prey relationships?
A) increased incidence of worm burrows in the fossil record
B) increased incidence of larger animals in the fossil record
C) increased incidence of organic material in the fossil record
D) increased incidence of hard body parts in the fossil record
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which vertebrates is fertilization exclusively internal?
A) chondrichthyans, osteichthyans, and mammals
B) amphibians, mammals, and reptiles
C) chondrichthyans, osteichthyans, and reptiles
D) reptiles and mammals
E) reptiles and amphibians
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arthropods invaded land about 100 million years before vertebrates did so. This most clearly implies that
A) arthropods evolved before vertebrates did.
B) extant terrestrial arthropods are better adapted to terrestrial life than are extant terrestrial vertebrates.
C) ancestral arthropods must have been poorly adapted to aquatic life and thus experienced a selective pressure to invade land.
D) vertebrates evolved from arthropods.
E) arthropods have had more time to coevolve with land plants than vertebrates have had.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The last common ancestor of all animals was probably a(n)
A) chytrid.
B) yeast.
C) algae.
D) fungus.
E) protist.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is (are) unique to animals?
A) cells that have mitochondria
B) the structural carbohydrate, chitin
C) nervous conduction and muscular movement
D) heterotrophy
E) flagellated gametes
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which clade does not include humans?
A) synapsids
B) lobe-fins
C) lophotrochozoans
D) tetrapods
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Whatever its ultimate cause(s) , the Cambrian explosion is a prime example of
A) mass extinction.
B) evolutionary stasis.
C) adaptive radiation.
D) a large meteor impact.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 88
Related Exams