A) 0.
B) 1.
C) infinity.
D) None of the above is correct.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Federal Reserve decreases the money supply, then initially there is a
A) shortage in the money market, so people will want to sell bonds.
B) shortage in the money market, so people will want to buy bonds.
C) surplus in the money market, so people will want to sell bonds.
D) surplus in the money market, so people will want to buy bonds.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
According to the theory of liquidity preference, the interest rate adjusts to balance the supply of, and demand for, loanable funds.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the interest rate increases, the opportunity cost of holding money
A) increases, so the quantity of money demanded increases.
B) increases, so the quantity of money demanded decreases.
C) decreases, so the quantity of money demanded increases.
D) decreases, so the quantity of money demanded decreases.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the theory of liquidity preference, if the interest rate rises
A) people want to hold more money. This response is shown by moving to the right along the money demand curve.
B) people want to hold more money. This response is shown by shifting the money demand curve right.
C) people want to hold less money. This response is shown by moving to the left along the money demand curve.
D) people want to hold less money. This response is shown by shifting the money demand curve left.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The multiplier effect
A) and the crowding-out effect both amplify the effects of an increase in government expenditures.
B) and the crowding-out effect both diminish the effects of an increase in government expenditures.
C) diminishes the effects of an increase in government expenditures, while the crowding-out effect amplifies the effects.
D) amplifies the effects of an increase in government expenditures, while the crowding-out effect diminishes the effects.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In response to the sharp decline in stock prices in October 1987, the Federal Reserve
A) increased the money supply and increased interest rates.
B) increased the money supply and decreased interest rates.
C) decreased the money supply and increased interest rates.
D) decreased the money supply and decreased interest rates.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Figure 34-10 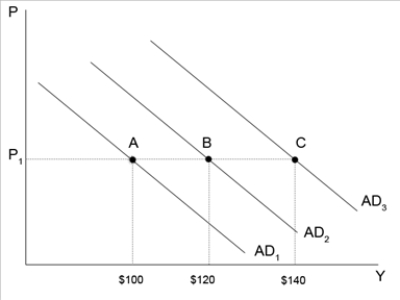 -Refer to Figure 34-10. Suppose the multiplier is 4 and the economy is currently at point A. An increase in government purchases of $10 will increase aggregate demand to $ if there is no crowding-out. If crowding- out exists, then aggregate demand will likely to increase to $ .
-Refer to Figure 34-10. Suppose the multiplier is 4 and the economy is currently at point A. An increase in government purchases of $10 will increase aggregate demand to $ if there is no crowding-out. If crowding- out exists, then aggregate demand will likely to increase to $ .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The main criticism of those who doubt the ability of the government to respond in a useful way to the business cycle is that the theory by which money and government expenditures change output is flawed.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 34-2. On the left-hand graph, MS represents the supply of money and MD represents the demand for money; on the right-hand graph, AD represents aggregate demand. The usual quantities are measured along the axes of both graphs.
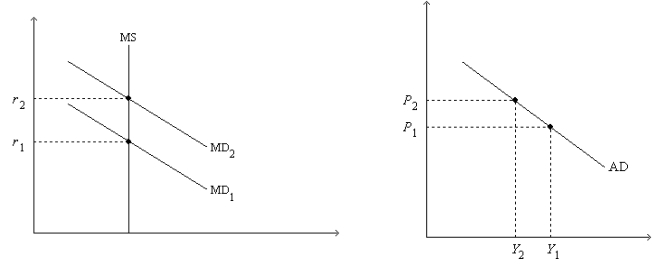 -Refer to Figure 34-2. What is measured along the horizontal axis of the left-hand graph?
-Refer to Figure 34-2. What is measured along the horizontal axis of the left-hand graph?
A) nominal output
B) real output
C) the opportunity cost of holding money
D) the quantity of money
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
The additional shifts in aggregate demand that result when there is an increase in government spending is known as the _____.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 34-8 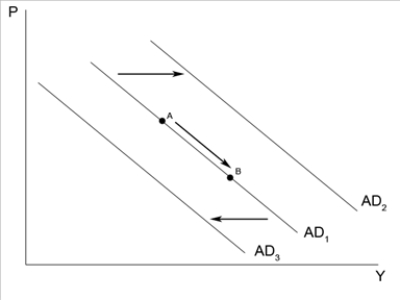 -Refer to Figure 34-8. An increase in government purchases will
-Refer to Figure 34-8. An increase in government purchases will
A) shift aggregate demand from AD1 to AD2.
B) shift aggregate demand from AD1 to AD3.
C) cause movement from point A to point B along AD1.
D) have no effect on aggregate demand.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose an increase in interest rates causes rising unemployment and falling output. To counter this, the Federal Reserve would
A) increase government spending.
B) increase the money supply.
C) decrease government spending.
D) decrease the money supply.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The lag problem associated with monetary policy is due mostly to
A) the fact that business firms make investment plans far in advance.
B) the political system of checks and balances that slows down the process of determining monetary policy.
C) the time it takes for changes in government spending to affect the interest rate.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The process of the investment accelerator involves
A) positive feedback from aggregate demand to investment.
B) negative feedback from aggregate demand to investment.
C) positive feedback from aggregate supply to investment.
D) negative feedback from aggregate supply to investment.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The interest rate that the Federal Reserve pays banks on the reserves they hold is called the
A) open-market rate.
B) discount rate.
C) preference rate.
D) None of the above are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the multiplier is 3, then the MPC is
A) 1/3.
B) 3/4.
C) 4/3.
D) 2/3.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Changes in monetary policy aimed at reducing aggregate demand involve decreasing the money supply or increasing the interest rate.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The interest-rate effect
A) depends on the idea that decreases in interest rates increase the quantity of goods and services demanded.
B) depends on the idea that decreases in interest rates decrease the quantity of goods and services demanded.
C) is responsible for the downward slope of the money-demand curve.
D) is the least important reason, in the case of the United States, for the downward slope of the aggregate- demand curve.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fiscal policy refers to the idea that aggregate demand is affected by changes in
A) the money supply.
B) government spending and taxes.
C) trade policy.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 511
Related Exams