A) Most waves are generated by earthquakes and become larger upon approaching the shore.
B) Most erosion along shorelines occurs from offshore currents.
C) Waves can erode, deposit, or simply transport sediment.
D) Tides increase and decrease the size of waves but leave sea level unchanged.
E) None of these.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If this spit continues to grow, cutting off the lagoon, it will become a 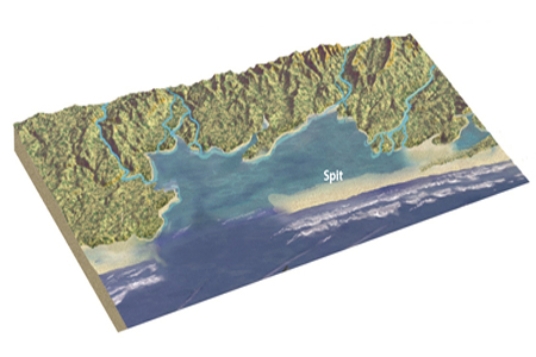
A) sandbar.
B) baymouth bar.
C) reef.
D) groin.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the primary reason an increase in glaciation on land would cause sea level to fall?
A) The temperature of the oceans decreases from cold glacial streams.
B) An increase in snow cover causes the atmosphere to heat up which causes more evaporation.
C) Glaciers depress the land surface, which pulls sea level down with it.
D) Glaciers tie up large volumes of water that would otherwise be in the sea.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following most likely indicates that sea level has risen relative to the land?
A) offshore sand bars that have become coastal dunes
B) the presence of coral reefs on land
C) wave-cut notches and platforms that are above sea level
D) marine terraces
E) an irregular coastline with branching estuaries and embayments
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With the Sun and Moon in this position, the side of the Earth facing the Moon experiences 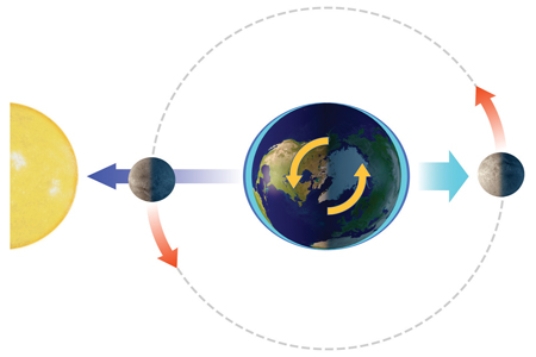
A) a normal high tide.
B) a normal low tide.
C) a spring tide.
D) a neap tide.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about how waves form and break upon the shore?
A) Most waves form from upwelling of deep waters.
B) Waves get smaller as wind speed increases.
C) Waves begin to change when they reach water shallower than wave base.
D) Waves break in a counterclockwise direction because of rotation of the Earth.
E) None of these.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If waves approach the shore at an angle they
A) die out before they reach the shore.
B) begin to break in water depths deeper than the wave base.
C) bend so they approach the shore more directly.
D) do none of these because waves do not approach the shore at an angle.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the rate of seafloor spreading along this ridge would cause 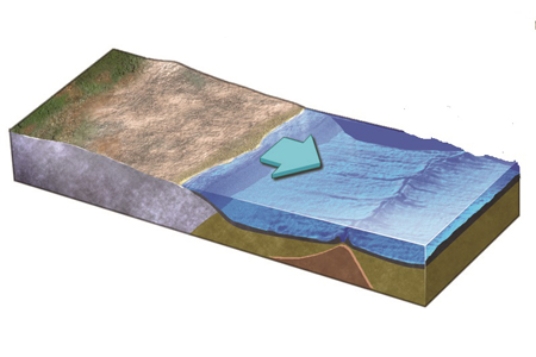
A) the ridge to become broader.
B) seawater to be displaced out of the ocean basin.
C) a rise in sea level.
D) All of these.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What geologic event is probably indicated by this irregular coast, with estuaries? 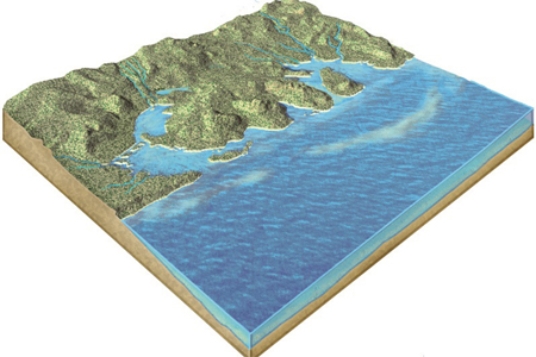
A) a rise in sea level
B) a drop in sea level
C) erosion due to large tsunamis
D) the uplift of submarine canyons
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Climate influences the processes along coastal landscapes by
A) controlling the amount of precipitation, which affects the amount of erosion.
B) affecting the size and intensity of storms.
C) allowing wet climates to support more vegetation which may stabilize the soil.
D) melting glaciers which causes sea level to rise.
E) All of these.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With the Sun and Moon in this position, the side of the Earth facing the moon experiences 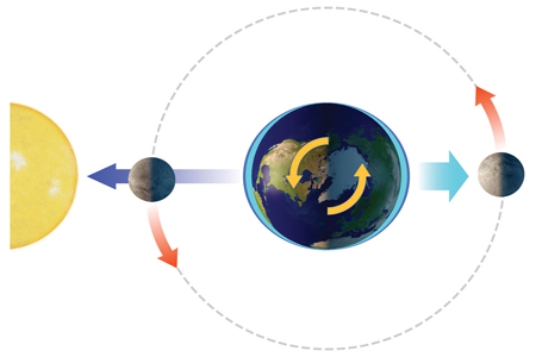
A) a normal high tide.
B) a normal low tide.
C) a spring tide.
D) a neap tide.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sand and other sediment
A) can move laterally along the coast if waves approach the beach at an angle.
B) only move up and down the slope of the beach.
C) can slump downward if the sea bottom has too gentle a slope.
D) are moved by the wind if the material is coarser than sand.
E) All of these.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is probably the least expensive approach for avoiding shoreline hazards?
A) bringing in sand to replenish what is lost to storms
B) using private insurance money to rebuild houses destroyed by erosion and waves
C) using federal disaster money to rebuild houses destroyed by erosion and waves
D) forbidding the building of houses or other structures in high-risk areas
E) building up the land level so communities, such as New Orleans, are above sea level
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
High tides are higher than average and low tides are lower than average when
A) the Moon and the Sun are aligned relative to the Earth.
B) it is a full moon.
C) it is a new moon.
D) All of these.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Factors that do NOT affect the appearance of a coast from the water side include
A) strength of waves and tides.
B) size and intensity of storms.
C) orientation of the coastline.
D) slope of the seafloor.
E) All of these affect the appearance.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An area will experience high tide
A) in the early afternoon when water temperatures are highest.
B) when there is a quarter moon in the sky.
C) when the moon is directly overhead or on the opposite side of Earth.
D) during a period of intense sunspot activity.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This wave-cut platform indicates 
A) a rise of sea level relative to the land.
B) a lowering of sea level relative to the land.
C) movement of a large thrust fault.
D) scouring of the land surface by a tsunami.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would cause sea level to rise?
A) a decrease in the number of glaciers on land
B) faster rates of seafloor spreading
C) a rise in the temperature of the oceans
D) All of these.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It has been proposed that the reason that the Pacific Ocean has many more coral reefs than the Atlantic Ocean is that
A) the Atlantic Ocean is too saline for many coral species.
B) the ocean currents in the Atlantic are too swift to allow for coral reefs to develop unimpeded.
C) the last glacial advance left the Atlantic too cold to allow coral to survive.
D) there are too many large rivers discharging polluted waters into the Atlantic basin to support as many coral reefs as in the Pacific, which is much larger and more immune to the pollution.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The left to right slope of the small island on the lower right of this photograph tells us that 
A) a nearby stream on the mainland must be providing sediment to support the island.
B) wave action must be minimal in this area.
C) an area of coastal upwelling must be nearby.
D) the ocean depth must be increasing to the right.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 64
Related Exams